Feature/OPED
Geopolitical Changes, African Union Reforms and Election of Next AU Commission’s Chairperson

By Professor Maurice Okoli
The African Union, a continental organisation, is heading for a new traditional face within the framework of its guiding principles. That new forthcoming era would open a new chapter and, to a large degree, determine the future of Africa, especially taking cognizance of the current global changes. In less than a year since the expiration of the African Union Chairperson’s position, an advanced search for the next candidate has begun. As stipulated by the organization’s constitution, the candidate for the powerful position is normally elected. It is tentatively planned to choose the fifth Chairperson to succeed incumbent Chairperson Moussa Faki, whose second term of office ends in February 2025.
The majority of African leaders have spoken of unprecedented reforms, carrying out a significant internal shake-up, and new blood to be pumped into the current African Union leadership and its related allied institutions. Arguments for several changes are necessary to make the continental organisation work more effectively and produce tangible results, especially now within the context of global reconfiguration. Africa is too diverse to fit together. But there are many more interests in uniting the continent. But the political, economic, and cultural diversities have to be transformed into continental strength to ensure development and growth, instead of a noticeable display of weaknesses and passive actions. It is often repeatedly claimed that the African Union needs urgent realistic reforms and some kind of rebranding of its structure as an effective instrument for rapid development, new economic architecture, and substantial growth.
In late January, Rwandan President Paul Kagamé was appointed to lead the AU institutional reform process. It was an important step towards implementing its institutional reforms, setting the Pan-African organisation’s objectives under the leadership of the Heads of State, who meet once a year at the Assembly. As Africa faces a multitude of crises, unstoppable debates have also dominated inside Africa and on international platforms over the performance of the 55-member organisation, its existing challenges, and the way forward in the fast-changing world.
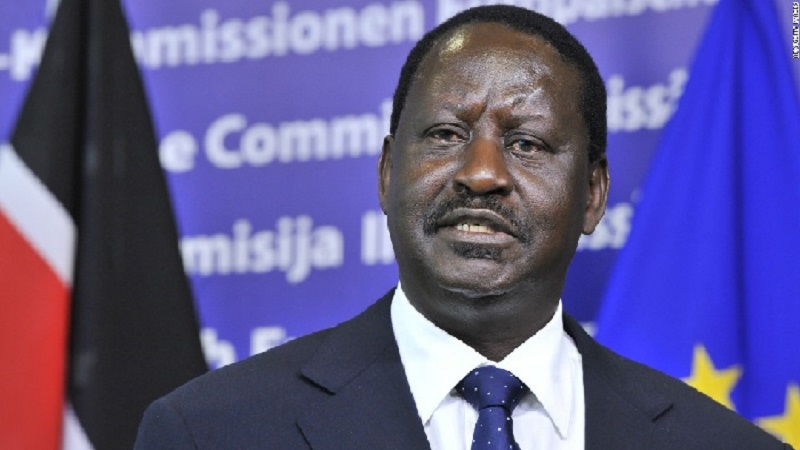
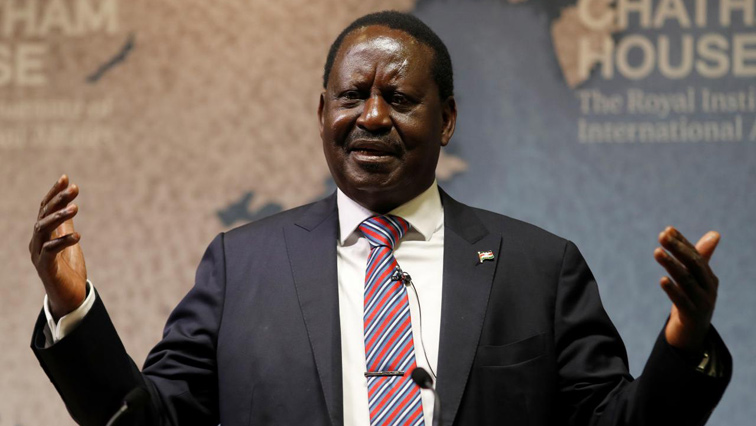
A media report released on March 3, 2024, titled “Museveni Endorses Raila Odinga’s AU Chairperson Bid” and circulated in the East African region showed the publicity campaign and erratic steps taken to promote Kenyan Raila Odinga to take over as Chairman of the AU Commission. Interestingly, Raila Odinga, Kenya’s opposition leader, has readily accepted Ugandan President Yoweri Museveni’s endorsement of his candidature for African Union Commission chairperson.
In a flagship statement posted via his social media platforms, Odinga said Museveni endorsed him during a joint meeting with President William Ruto. The Azimio alliance’s leader stated that the joint meeting with President Museveni and President Ruto was organized at the Ugandan president’s invitation.
“I accepted an invitation from President Yoweri Kaguta Museveni of Uganda for a joint meeting with President William Samoei Ruto. President Museveni strongly endorsed my candidature for Chairperson of the African Union Commission,” said Odinga, showing appreciation for William Ruto for fully supporting his candidature.
The trio also discussed the AU platform for deepening regional integration within the East African Community. Apart from Presidents Ruto and Museveni, other state heads who threw their invaluable weight behind the former Prime Minister are Samia Suluhu (Tanzania), Cyril Ramaphosa (South Africa), Salva Kiir (South Sudan), and Felix Tshisekedi of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. In addition, former Nigerian President Olusegun Obasanjo also endorsed Odinga, saying he is the best candidate to replace the outgoing chair, Moussa Faki.
Raila Odinga has an unmistakable political influence. He was born into a modest political family and grew up in politics. His profound perspectives suggest he operates as a pivotal figure within power dynamics, and his decision-making capacity is perceived as absolutely pragmatic. Odinga, most observers say, possesses an assertive leadership style and always expresses a steadfast interest in the complexity of a development-oriented society. These leadership skills echo his deep-seated affection for a genuine communal, regional, and continental tradition. Odinga as a suitable candidate underscores the perfect choice to embrace and settle for the best administrator for Africa.
Nevertheless, an insight into the choice and nomination of possible candidates is fraught with intrigue and nepotism. But at a glance, Odinga envisions carving out a new, distinctive image for the African Union. His high-value knowledge and experiences, corporate business entrepreneurialism, and pragmatic new economic development thinking would probably save Africa. Narratives too indicated that Odinga would adopt a far-reaching overhauled approach and take unshakable measures towards the most significant issues across Africa. These are essential conditions for re-imaging the AU’s future.
As the history of the stipulated procedures indicates, the elected chairperson becomes the head of the African Union Commission. For instance, on January 30, 2017, after seven rounds of voting, Chad’s Moussa Faki Mahamat was elected chairperson over Nigeria’s Amina Mohamed. He was re-elected in 2021 for another four-year term, which ends in 2025. Moussa Faki Mahamat, born on June 21, 1960, was first elected as the African Union Commission (AUC) Chairperson on January 30, 2017, and assumed office in March 2017. He served previously as State Minister of Foreign Affairs for the Republic of Chad.
According to official documents researched, the Chairperson of the AUC is the Chief Executive Officer, the legal representative of the AU, and the Commission’s Chief Accounting Officer. The Chairperson of the Commission is elected by the Assembly for a four-year term, renewable once.
In broad terms, the Chairperson’s functions include overall responsibility for the Commission’s administration and finances; promoting and popularising the AU’s objectives and enhancing its performance; consulting and coordinating with key stakeholders like member states, development partners, and Regional Economic Communities (RECs); appointing and managing the Commission’s staff; and acting as a depository for all AU and OAU treaties and legal instruments.
The African Union (AU) under Moussa Faki Mahamat has made several achievements, including raising the continental external relations profile and its ascension into the Group of Twenty (G20). In September 2023, when Prime Minister Narendra Modi of India chaired the G20 summit, the G20 nations agreed to grant the African Union permanent membership status in an appreciable move aimed at offering the continent a stronger voice on important questions and to uplift its status on a higher stage. In its final declaration in New Delhi, the G20 granted the African Union full membership. The G20 consists of 19 countries and the European Union, making up about 85 percent of the global GDP and two-thirds of the world’s population.
New Delhi is also counting on earning high-profile PR points to burnish its reputation as a Global South leader. In an article published in Indian and foreign newspapers ahead of the summit, Modi wrote, “Our presidency has not only seen the largest-ever participation from African countries but has also pushed for the inclusion of the African Union as a permanent member of the G20.”
Under Moussa Mahamat’s African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), the single continental market has the potential to unite an estimated 1.4 billion people in a $2.5 trillion economic bloc. The AfCFTA opens up tremendous opportunities for both local African and foreign investors from around the world.
January 1, 2021, signaled the commencement of Africa’s journey to market integration after it was postponed by six months in 2020 following the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic. But its huge potential, which cannot be underestimated, is to generate a range of benefits through supporting trade creation, structural transformation, productive employment, and poverty reduction.
It aims at making Africa the largest common market in the world and accelerating continental integration. It is expected to reinforce the measures taken in terms of the free movement of persons, goods, and services across borders. But much depends on the collective determination and solidarity demonstrated by African leaders to face the challenges in a united and resolute manner. It depends on the strong mobilization of African leaders and the effective coordination provided by the African Union.
For this to be successful, Africa has to engage in modernising agriculture and strengthening agro-food systems by working towards its food security rather than simply accepting food packages as ‘gifts’ from so-called external friends. The next stage is to industrialise, add value to the agricultural products by processing them, and finally distribute them locally and for exports, hence the establishment of the AfCFTA. From this concrete perspective will emerge a new Africa, “the Africa we want,” which has understandably become the resounding guiding slogan.
Despite that, there have also been several critical assessments and careful analyses of developments over the past few years. The AU has made scathing remarks on the negative impacts inflicted by imperialism, neocolonialism, and Western hegemony. And further consistently called for calling for a complete overhaul of the multinational financial system to enable the pursuit of needed development goals across Africa. Paradoxically, Africa has huge resources, both natural and human, but the larger size of its population still lives in abject poverty and desperation.
At least a majority of African leaders on their side recognised the need to reform the continental organisation too. It has allegedly been manipulated by external powers, and to a large extent, internal deficiencies and weaknesses are still persistent on the continent. These include the absence of the fundamentals of democracy, good governance, transparency, and accountability, primarily due to weak institutions and ineffective organs of the state, especially the parliaments. Opposition groups are stifled, putting democracy at risk across Africa.
Rising ethnic conflicts, political-economic instability, and military appearance in politics. These have sparked widespread mass protests. Burkina Faso, Chad, Guinea, Gabon, Mali, and Niger are run by military officers. Then there was instability in Libya, Somalia, Sudan, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). The biggest vulnerabilities include the proliferation of weapons, weak border control, and unprotected industrial facilities. The inevitable impact on the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals.
Researchers say the African Union should dedicate this year to solving the various issues of instability and restoring credibility in the democratic process. Non-constitutional changes of government have multiplied in total defiance of the entire political and legal system on which the organization was founded. Never since the creation of the African Union has there been such a large number of transitions following unconstitutional changes of government in Africa. (See African Leaders Extraordinary Summit report, February 2024.)
Set up more than two decades ago, the 55-member bloc has long been criticized for being ineffectual and for taking little decisive action in the face of numerous power grabs. Some 19 presidential or general elections are scheduled on the continent in 2024, portending more challenges for the AU.
Seemingly, there is a necessity to navigate a new dynamic development paradigm within the context of multipolar relations. The multifaceted nature of obstacles has to be addressed with a spirit of vigour and valuable perspectives. There are three main directions: democracy and good governance, food security and industrialization, and economy and trade. These could lead to social inclusion and broadening employment for the youth and the next generation. They could also lead to economic growth, stability, and better life conditions across Africa. All aspects of Africa’s development are incorporated into the joint report published at the African Economic Conference 2022.
In a nutshell, the African Union and African leaders have to realign their foreign policies and back away from geopolitical insinuations, rather than take advantage of the complexities and confrontations to look for substantive opportunities to support their efforts in pursuit of building better. The beauty of Africa lies not only in its economic potential but also in its vibrant and diverse cultures.
However, it would be remiss to discuss Africa’s economic growth without addressing the challenges that persist. Poverty, inequality, and a lack of infrastructure continue to hinder progress. It is our collective responsibility to work towards addressing these issues, ensuring that the benefits of Africa’s economic growth are inclusive and sustainable.
Notwithstanding the questions raised above, Moussa Faki Mahamat has spoken of “worrying trends” during these past few years at high-level conferences and meetings, characterising the main challenges “as political instability, climate change, poverty, deficits in economic governance, and marginalisation of women and young people in development and leadership.” Another major subject of discussion has been how the AU will transition to relying on African states to fund most of its budget rather than foreign donors. For instance, the UN Security Council in December adopted a resolution to finance AU-led peace missions but capped it at 75 percent of the budget.
The 37th AU Ordinary Session of the Assembly of Heads of State and Government, at the annual convention in February 2024, stressed the necessity for practical long-term strategies and to strengthen efforts at achieving peace and stability on the continent and to attain the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and AU Agenda 2063. The AU Agenda 2063 is a comprehensive development framework for Africa.
The significant aspect of the retreat was the valuable discussions on the reform agenda. The reform agenda emphasises the need to focus on key priorities with a continental scope, realigning AU institutions to deliver on its objectives, operational efficiency, and sustainable self-financing of the Union. The retreat also reviewed the second ten-year plan of Agenda 2063, which spans from 2024 to 2033.
In the context of a multipolar geopolitical order, African leaders and the African Union should strengthen their positions regarding external partnerships. The African Union has to take up the task of developing collective approaches to the problems of maintaining peace and security, strengthening democratic processes, developing human potential, and ensuring socio-economic growth. If not, the continent risks being left behind and used as a pawn in an increasingly divided global order.
The African Union has, in a parallel direction, spearheaded Africa’s development and integration in close collaboration with African Union Member States, the Regional Economic Communities, and African citizens. The AU’s vision is to accelerate progress towards an integrated, prosperous, and inclusive Africa, at peace with itself, playing a dynamic role in the continental and global arenas, effectively driven by an accountable, efficient, and responsive Commission. These are incorporated into a single continental development program referred to as the AU Agenda 2063.
Professor Maurice Okoli is a fellow at the Institute for African Studies and the Institute of World Economy and International Relations, Russian Academy of Sciences. He is also a fellow at the North-Eastern Federal University of Russia. He is an expert at the Roscongress Foundation and the Valdai Discussion Club.
As an academic researcher and economist with a keen interest in current geopolitical changes and the emerging world order, Maurice Okoli frequently contributes articles for publication in reputable media portals on different aspects of the interconnection between developing and developed countries, particularly in Asia, Africa, and Europe. With comments and suggestions, he can be reached via email: markolconsult (at) gmail (dot) com.
Feature/OPED
$214Bn Missing, Institutions Silent: Is Accountability Dead in Nigeria?

By Blaise Udunze
Between 2010 and 2026, a staggering $214 billion, approximately N300 trillion in public funds, has been reported as missing, unaccounted for, diverted, unrecovered, irregularly spent, or trapped in non-transparent fiscal structures across Nigeria’s public institutions.
That figure is not speculative but a conservative estimate of unaccounted funds. It is drawn from audit reports, legislative probes, civil society litigation, executive directives, and investigative findings spanning more than a decade. If it is to go by the accurate figure, the true national loss is likely higher but difficult to quantify precisely due to data gaps, overlapping figures, and incomplete audits.
The challenge is that in many of the most prominent cases, prosecutions have stalled, hearings have dragged without resolution, investigations have gone cold, and no defining jail terms have etched accountability into Nigeria’s institutional memory. The irony is that the number is historic, the silence is louder. And the economic damage is cumulative.
The pattern stretches from the oil sector to social investment programmes, from the Nigeria Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) interventions to ministry-level expenditures. In 2014, between $10.8 billion and $20 billion in unremitted oil revenues linked to the Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation triggered national outrage. Under the then CBN governor, Lamido Sanusi, who warned that persistent oil revenue leakages were making exchange rate stability “extremely difficult.” He cautioned that without full remittances, the alternative would be currency devaluation and financial instability. This concern spans the 2010 to 2013 oil revenue period. That warning proved prophetic.
This is because, years later, the lack of transparency in the oil industry did not disappear, but rather it festered like cancer. It further led to the elongated audit queries, which have continued to trail the Nigerian National Petroleum Company Limited, including unremitted revenues, questioned deductions, and management fee structures under the Petroleum Industry Act. With an extraordinary move aimed at blocking revenue leakages at source, President Bola Ahmed Tinubu has recently issued an Executive Order suspending certain deductions and directing direct remittance of taxes, royalties, and profit oil into the Federation Account, which involves the reassessment of NNPC’s 30 per cent management fee and 30 per cent frontier exploration deduction under the Petroleum Industry Act.
Such presidential intervention underscores the scale of concern, which means that Nigeria cannot afford a structural lack of transparency in its most strategic revenue sector. But oil is only one chapter.
The Central Bank of Nigeria has faced some of the most far-reaching audit alarms in recent years. In suit number FHC/ABJ/CS/250/2026, the Socio-Economic Rights and Accountability Project (SERAP) is asking the Federal High Court to compel the CBN to account for N3 trillion in allegedly missing or diverted public funds. The Auditor-General’s 2025 report cited failures to remit over N1.44 trillion in operating surplus to the Consolidated Revenue Fund, over N629 billion paid to “unknown beneficiaries” under the Anchor Borrowers’ Programme, and more than N784 billion in overdue, unrecovered intervention loans.
There were also N125 billion in questioned intervention expenditures, irregular contract variations exceeding N9 billion, and procurement gaps running into hundreds of billions. The Auditor-General repeatedly recommended recovery and remittance. No date has been fixed for the hearing. Meanwhile, Nigeria continues to borrow.
Elsewhere, the House of Representatives has launched a probe into over N30 billion recovered during investigations into the National Social Investment Programme Agency (NSIPA). The funds, reportedly frozen during investigation, have not been remitted back into the Treasury Single Account, stalling poverty-alleviation schemes like TraderMoni and FarmerMoni. Millions of vulnerable Nigerians remain exposed while lawmakers search for money already “recovered.” The irony is staggering as funds are found, but programmes remain frozen.
A top discovery recently that put the nation on red alert was made by the Senate committee, which claimed to have found N210 trillion in financial irregularities in NNPC accounts between 2017 and 2023, including unaccounted receivables and accrued expenses. A critical concern is that, as of early 2026, this has sparked commentary but no clear prosecutions.
Only recently, in the power sector, SERAP has urged the President to probe alleged missing or unaccounted N128 billion at the Federal Ministry of Power and the Nigerian Bulk Electricity Trading Plc. Of concern is that despite the enormous funds channelled in this sector, Nigeria’s chronic electricity instability persists, even as billions meant to stabilise the grid face audit scrutiny.
Across MDAs, audit reports between 2017 and 2022 flagged trillions in unsupported expenditures, unremitted taxes, unauthorised payments, and statutory liabilities never recovered. These sums are dizzying and are also alarming; N300 billion here, N149 billion there, N3.403 trillion across agencies, N30 trillion-plus Treasury discrepancies raised at the Senate level.
Individually, they shock. Collectively, they define a structural pattern. And patterns shape economies.
Nigeria operates with structural fiscal deficits and also lives with them routinely and comfortably. Expenditure persistently exceeds revenue. When public funds disappear, fail to be remitted, or are trapped outside constitutional channels, the deficit widens. The government must borrow to fill gaps created not only by low revenue, but by revenue leakage.
Debt servicing now consumes a disproportionate share of federal revenue. Borrowing meant for capital projects increasingly finances recurrent obligations. The country shifts from borrowing to build to borrowing to survive. Every missing naira compounds tomorrow’s liability.
The Treasury Single Account (TSA) was designed to plug such leakages. It consolidated government revenues under Section 80 of the Constitution into a unified framework. International financial institutions commended it as a landmark reform. Yet even today, the Minister of Finance, Wale Edun, has admitted that substantial government funds remain outside the TSA and outside the CBN’s consolidated visibility. Until August 1, 2024, he revealed, the federal government could not fully see its own balance sheet at the apex bank. That admission should alarm any serious economy.
Fiscal lack of transparency constrains planning. It undermines monetary coordination. It weakens debt sustainability projections. It distorts policy responses. And when systems are in flux, money vanishes more easily.
Changing or weakening the TSA in such an environment would be catastrophic. Transitions create windows of vulnerability. Old accounts close. New accounts open. Reconciliation’s lag. Ghost contractors reappear. Double payments slip through.
Albeit, the government must learn to tread with caution as Nigeria’s institutional bandwidth is already strained by simultaneous tax reforms, exchange-rate adjustments, subsidy removal, and fiscal restructuring. One truth that cannot be argued is that layering additional structural upheaval onto fragile systems risks revenue loss that the country cannot afford. Investors are watching.
Credit markets evaluate not just numbers but institutional consistency. A nation that abandons or weakens its most credible fiscal reform sends a destabilising signal. Stability lowers borrowing costs. Institutional drift raises them. But beyond markets lies the human cost.
N300 trillion represents roads not built, power plants not completed, irrigation systems not funded, schools not modernised, and hospitals not equipped. It represents jobs not created and industries not catalysed. It represents stalled productivity and deferred growth.
When intervention loans remain unrecovered, agricultural output suffers. When power sector funds are unaccounted for, electricity remains unstable. When social investment funds are frozen, poverty deepens.
Inflation then compounds the pain. Revenue gaps push borrowing. Borrowing pressures, interest rates and by extension, liquidity misalignment fuel price instability. Citizens pay through higher food costs, transport fares, and rent. The poor pay first. The middle class erodes quietly.
Perhaps most corrosive is the trust deficit. When audit queries fade without visible accountability, tax morale weakens. Compliance declines. Cynicism hardens. A nation cannot modernise where trust in fiscal integrity is fragile.
Section 15(5) of the Constitution requires the abolition of corrupt practices. Financial Regulations mandate a surcharge and referral to anti-corruption agencies where public officers fail to account for funds. The Fiscal Responsibility Act empowers citizens to enforce compliance to ensure that government officials follow fiscal rules. But enforcement defines seriousness.
Nigeria’s problem is not a lack of audit findings. It is the distance between findings and finality.
Nations do not collapse overnight due to a lack of funds. They drift. Infrastructure decays incrementally. Debt rises gradually. Growth slows subtly. Confidence erodes quietly. Then one day, stagnation feels permanent. $214 billion (N300 trillion), sixteen years of recurring audit alarms. Few conclusive accountability outcomes are proportionate to the scale. Truly, the consequences have been less strong. For the same reason, the country witnessed President Tinubu nominating ex-NIA boss Ayodele Oke as ambassador despite a $43 million loot in an Ikoyi apartment.
See the research breakdown of some of the audit figures that reveal staggering sums as enumerated above:
– $10.8 billion and separately $20 billion in unaccounted oil revenues at the NNPC in 2014
– $1.1 billion controversial Malabu Oil and Gas oil deal in 2015
– $2.2 billion arms procurement irregularities in 2015
– N3.4 billion from IMF COVID-19 financing flagged in a 2020 audit.
– N149.36 billion, N37.2 billion, and multiple irregular MDA expenditures in 2020 alone.
– N300 billion cited in public audit concerns in 2017.
– N210 trillion in financial irregularities uncovered, N103 trillion in ‘accrued expenses’, and another N107 trillion in unaccounted ‘receivables’ (2017 -2023).
– N57 billion Ministry of Humanitarian Affairs – (2021)
– N3 trillion and N1.44 trillion flagged in 2022 audit issues involving the Central Bank of Nigeria.
– Nearly N630 billion under the Anchor Borrowers Programme is reportedly unrecovered.
– N784 billion in overdue intervention loans flagged.
– Over N3.403 trillion unaccounted for across federal MDAs between 2019 and 2021.
– Roughly 30 trillion+ in Treasury Single Account and Consolidated Revenue Fund discrepancies raised at the Senate level.
– N500 billion in unremitted oil revenues between 2019 and 2024.
– N80 billion tied to alleged fictitious contracts in the Accountant-General’s office.
– N69.9 billion in uncollected statutory tax liabilities.
– Billions more in unauthorised or undocumented expenditures across ministries.
The institutions differ. The years differ. The audit language differs. The pattern does not.
Nigeria’s economic future will not be determined solely by how much oil it produces, how many reforms it announces, or how many executive orders it signs. It will be determined by whether every naira earned enters the Federation Account transparently, whether every intervention loan is tracked and recovered, whether every surplus is remitted constitutionally, and whether every diversion carries consequences. Revenue generation matters. Revenue protection is destiny. Because when government funds go missing, nations do not stand still. They move backwards.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: bl***********@***il.com
Feature/OPED
The Hidden Workforce of the 2026 Access Bank Lagos City Marathon
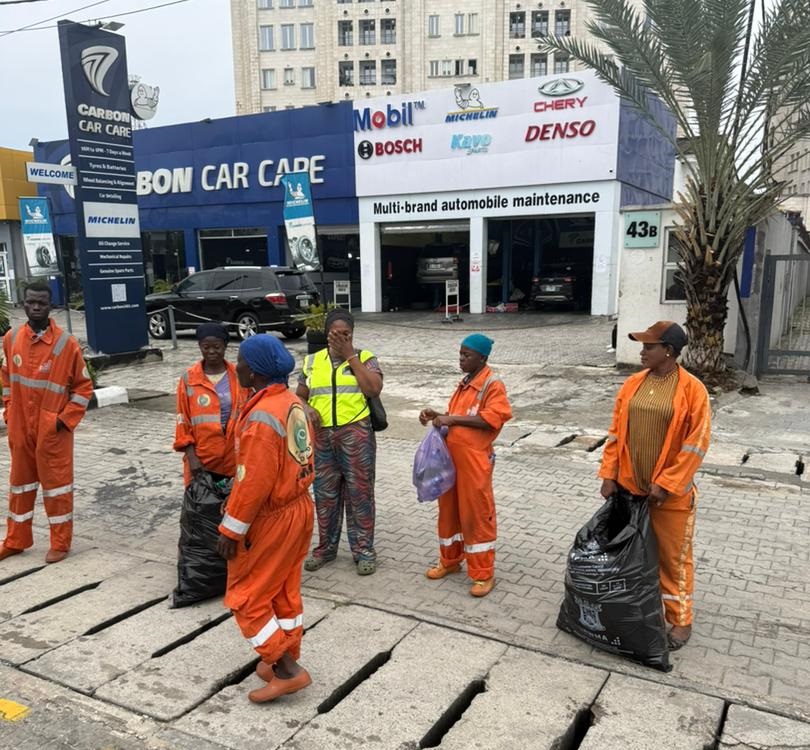

When the final runner crossed the finish line at the 11th edition of the Access Bank Lagos City Marathon (ABLCM), the applause began to fade. But for hundreds of workers across Lagos, the real work was just beginning.
Major highways had been closed to facilitate the event. Tens of thousands of runners moved through the city in a coordinated surge of athletic endurance. Thousands of bottles of water and energy drinks were distributed, alongside sachets containing essential medical supplies and medication. The race route itself was meticulously prepared, lined with banners, barricades, medical tents and precision timing systems that ensured safety, organisation and accurate performance tracking from start to finish.
What followed was the part that a few cameras lingered on, yet it remains one of the clearest indicators of institutional progress.
Within minutes of the race conclusion, coordinated sanitation teams fanned out across the marathon corridor. Their work went beyond sweeping. Waste was systematically sorted. Plastic bottles were separated from general refuse. Sachets were gathered in bulk. Collection trucks moved along predefined routes, ensuring rapid evacuation of waste. Temporary race infrastructure was dismantled with quiet precision.
In a megacity like Lagos, speed is a necessity. Urban momentum cannot pause for long. The ability to restore order quickly after an event of this magnitude reflects operational discipline across interconnected systems, municipal authorities, environmental agencies, private waste management partners and event coordinators.
Globally, large-scale sporting events are no longer evaluated solely by participation numbers or prize purses. Sustainability has emerged as a defining metric. Environmental responsiveness is now a core measure of credibility. Cities seeking tourism growth, foreign investment and international partnerships must demonstrate that scale does not compromise responsibility. The 2026 marathon provided a compelling case study in this evolution.
The clean-up operation itself generated meaningful economic activity. Temporary employment opportunities emerged for sanitation workers and logistics personnel. Recycling partners engaged in material recovery, reinforcing circular economy value chains. What was once viewed as routine waste disposal has evolved into a structured ecosystem of environmental services, a sector of increasing importance in modern urban economies.
This level of sustainability was the result of deliberate planning. Effective post-event recovery requires route mapping, waste volume projections, coordination between sponsors such as Access Bank Plc and municipal bodies, contingency planning for congestion points and clear communication protocols.
Each edition of the marathon has built on lessons from the last. International participation has expanded. Accreditation standards have strengthened. Media visibility has grown. Most importantly, environmental management has become embedded in the marathon’s operational framework rather than treated as an afterthought.
Progress rarely arrives in dramatic leaps, it advances through incremental improvements, refined systems and institutional learning. Just as elite runners close performance gaps through disciplined training, cities strengthen their global standing through consistent operational excellence.
The 2026 marathon, therefore, tells a story that extends far beyond athletic achievement. It is a story of coordination, sustainability as strategy rather than slogan, and the often unseen workforce, sanitation workers, planners, volunteers, security officials and environmental partners, whose discipline sustains the spectacle.
Because in the end, global cities are judged by how well they host and how responsibly they restore. On the marathon day in Lagos, it was the runners who demonstrated endurance and the systems, and the people behind them, who ensured that when the cheering stopped, the city kept moving.
Feature/OPED
N328.5bn Billing: How Political Patronage Built Lagos’ Agbero Shadow Tax Empire

By Blaise Udunze
Lagos prides itself as Africa’s commercial nerve centre. It markets innovation, fintech unicorns, rail lines, blue-water ferries, and billion-dollar real estate. Though with the glittering skyline and megacity ambition lies a parallel state, a shadow taxation regime run not from Alausa, but from motor parks, bus stops, and highway shoulders. They are called “agberos.” And for decades, they have functioned as Lagos’ unofficial tax masters.
What began as loosely organised transport unionism mutated into a pervasive and often violent system of extortion. Today, tens of thousands of commercial buses, over 75,000 danfos according to estimates by the Lagos Metropolitan Area Transport Authority, ply Lagos roads daily. Each bus is a moving ATM. Each stop is a tollgate. Each route is a revenue corridor.
Looking at the daily estimate from their operations, at N7,000 to N12,000 per bus per day, conservative calculations show that between N525 million and N900 million is extracted daily from drivers. Annually, that balloons toward N192 billion to N328.5 billion or more, money collected in cash, unreceipted, unaudited, unaccounted for. This illicit taxation on an industrial scale did not emerge in a vacuum.
The reality today is that to understand the scale of the problem, one must confront its political history. It was during the administration of Bola Ahmed Tinubu as Lagos State governor from 1999 to 2007, who is now the President, that the entrenchment of transport union dominance and motor park patronage deepened.
Under his political machine, transport unions became not just labour associations but mobilisation structures, formidable grassroots networks capable of crowd control, voter turnout engineering, and territorial enforcement. In exchange for political loyalty, street influence translated into operational latitude.
Motor parks became power bases. “Area boys” became enforcers. Union leadership became politically connected. What should have been regulated associations morphed into revenue-generating franchises with muscle.
The system outlived his tenure. It institutionalised itself. It professionalised. It is embedded in Lagos’ political economy.
And today, it thrives in broad daylight. Endeavour to visit Ajah under bridge, Ikeja under bridge, or Mile-2 along Ojo at 6:00 a.m. Watch drivers clutching crumpled naira notes. Observe men in green trousers and caps marked NURTW weaving between buses, collecting what drivers call òwò àrò, or evening as òwò iròlè money taken from passengers.
A korope driver shouts, “Berger straight!” His bus fills. The engines rumble. But before he moves, he must pay. If he refuses? The side mirror may disappear. The windscreen may crack. The conductor may be assaulted. The vehicle may be blocked with planks, and if they resist, the conductor or driver may be beaten. Movement becomes impossible. It is not optional.
This is common across Lagos, especially amongst drivers in Oshodi, Obalende, Ojodu Berger, Mile 2, Iyana Iba, and Badagry, and describes a three-layered structure ranging from street collectors, area coordinators, and union executives at each location. Daily targets flow upward. Commissions remain below.
One conductor disclosed he budgets at N8,500 daily for louts alone, excluding fuel, delivery to vehicle owners, and official tickets. Another driver says he parts with nearly N15,000 in total daily levies across routes.
Of N40,000 collected on trips, barely N22,000 survives before fuel. Sometimes, drivers go home with N3,500. Working like elephants. Eating like ants. The impact extends far beyond drivers.
Every naira extorted is transferred to commuters. An N700 fare becomes N1,500. A N400 corridor becomes N1,200 in traffic, and this is maintained even after fuel prices fall; fares rarely decline. The hidden levy remains.
Retail traders reduce stock purchases because transport eats profits. Civil servants watch salaries stagnate while commuting costs climb. Market women complain that surviving Lagos costs more than living in it.
This is not just a transport disorder. It is inflation engineered by coercion. Economists call it financial leakage, money extracted from the productive economy that never enters the fiscal system. Billions circulate annually without appearing in government ledgers. No roads are built from it. No hospitals funded. No schools renovated.
It is taxation without development. Small and Medium Enterprises form nearly half of Nigeria’s GDP and employ the majority of its workforce. In Lagos, they are under assault from informal levies layered on top of official taxes. Goods delivered by bus carry hidden transport premiums. Commuting staff face higher daily costs. Inflation ripples through supply chains.
The strike by commercial drivers in 2022 exposed the depth of resentment. Under the Joint Drivers’ Welfare Association of Nigeria (JDWAN), drivers protested “unfettered and violent extortion.” Lagos stood still. Commuters trekked. Appointments were missed. Businesses stalled.
Drivers alleged that half of their daily income vanished into motor park collections.
Some who protested were attacked. Yet the collections continued.
Drivers insist daily collections at single corridors can exceed N5 million. Park chairmen allegedly control enormous cash flows. Uniformed collectors operate with visible confidence.
Meanwhile, the Lagos State Government denies sanctioning any roadside extortion. Officials describe the tax system as institutionalised and structured. They promise reforms through Bus Rapid Transit, rail expansion and corridor standardisation. Yet the shadow toll persists.
Contrast this with Enugu State, where Governor Peter Mbah introduced a Unified e-Ticket Scheme mandating digital payments directly into the state treasury. Paper tickets were banned. Cash collections outlawed. Revenue flows are traceable. Harassment criminalised.
Drivers in Lagos say openly that they should be given a single N5,000 daily ticket paid directly to the government, and end the chaos. Instead, they face multiple actors, agberos, task forces, and traffic officials, each demanding settlement.
The difference is in governance philosophy. One digitises and centralises revenue to eliminate leakages.
The other tolerates fragmentation that breeds shadow collectors. The uncomfortable truth is that the agbero structure is politically sensitive. Transport unions are not just labour bodies; they are political instruments. They mobilise during elections. They maintain territorial presence. They command street loyalty. In return, they are allegedly tolerated, protected, or absorbed into broader political structures as they turn into war instruments and a battle axe in the hands of the government of the day. The underlying reality is that the agbero who are the street-level power structures and the government authorities benefit from each other; the line between unofficial influence and official governance becomes unclear, making reform politically sensitive.
The issue is not merely about street disorder; it is about economic governance. Illicit taxation distorts pricing mechanisms, reduces productivity, discourages the formalisation of businesses, and weakens public trust. If citizens are compelled to pay both official taxes and unofficial levies, compliance morale declines. Why comply with statutory taxation when parallel systems operate unchecked?
Dismantling them is not merely administrative; it is political. Perhaps unbeknownst to the people, the cost of inaction is immense. Lagos aspires to be a 21st-century smart megacity under such an atmosphere. But investors notice informal roadblocks. Businesses factor in unpredictability. Commuters absorb unofficial taxes daily. Across Lagos roads, the script repeats “òwò mi dà,” meaning, give me my money.
Passengers plead with collectors to reduce levies so they can proceed. Conductors argue over dues before departure. Citizens feel hostage to a system they neither elected nor authorised.
Taxation, constitutionally, belongs to the state. It must be legislated, receipted, audited and deployed for the public good.
Agbero taxation is none of these. It is coercive. It is not transparent. It is extractive. Lagos has launched rail lines and BRT corridors. The Lagos Metropolitan Area Transport Authority continues transport reforms. Officials promise that bus reform initiatives will eliminate unregistered operators. But reform cannot be selective. You cannot modernise rail while medieval tolling persists on roads. You cannot preach digital governance while cash collectors flourish at bus stops. You cannot aspire to global city status while informal muscle dictates movement.
The solution is not episodic arrests. It is a structural overhaul: mandatory digital ticketing across all parks; a single harmonised levy payable electronically; an independent audit of union revenue; protection for drivers who resist illegal collections; and political decoupling of unions from patronage networks.
The agbero empire is not merely about bus fares. It is about how patronage systems, once empowered, metastasise into parallel authorities. What may have begun as strategic alliance-building two decades ago has matured into a shadow fiscal regime embedded in daily life.
The challenge is that Lagosians are left with no choice as they now pay twice, once to the government, once to the streets. And unlike official taxes, shadow taxes leave no developmental footprint. No bridge bears their name. No hospital wing testifies to their billions. No classroom is built from their collections. Only inflated fares. Broken windscreens. Frustrated commuters. And drivers who sweat under the sun, calculating how much will remain after everyone has taken their cut.
The agbero question is ultimately a governance question. Is Lagos governed by law, or by tolerated coercion? Is taxation a constitutional function, or a roadside negotiation? Is political convenience worth permanent economic distortion? What is absolutely known is that the structure has a political backing and what politics created, politics can dismantle.
Unless meaningful reform takes place, Lagos will continue to remain a megacity with a shadow treasury, where movement begins not with ignition, but with payment to men who answer to no ledger without any tangible returns. This is to say that every danfo that moves carries not just passengers, but the weight of a system that taxes without law, collects without accountability and punishes the very people who keep the city alive.
Blaise, a journalist and PR professional, writes from Lagos and can be reached via: bl***********@***il.com
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn