Health
mPharma Launches Programme to Tackle Hypertension in Nigeria, Others
By Adedapo Adesanya
mPharma has launched the Hypertension Test and Treat programme (HTT) to support the prevention and control of hypertension in Africa.
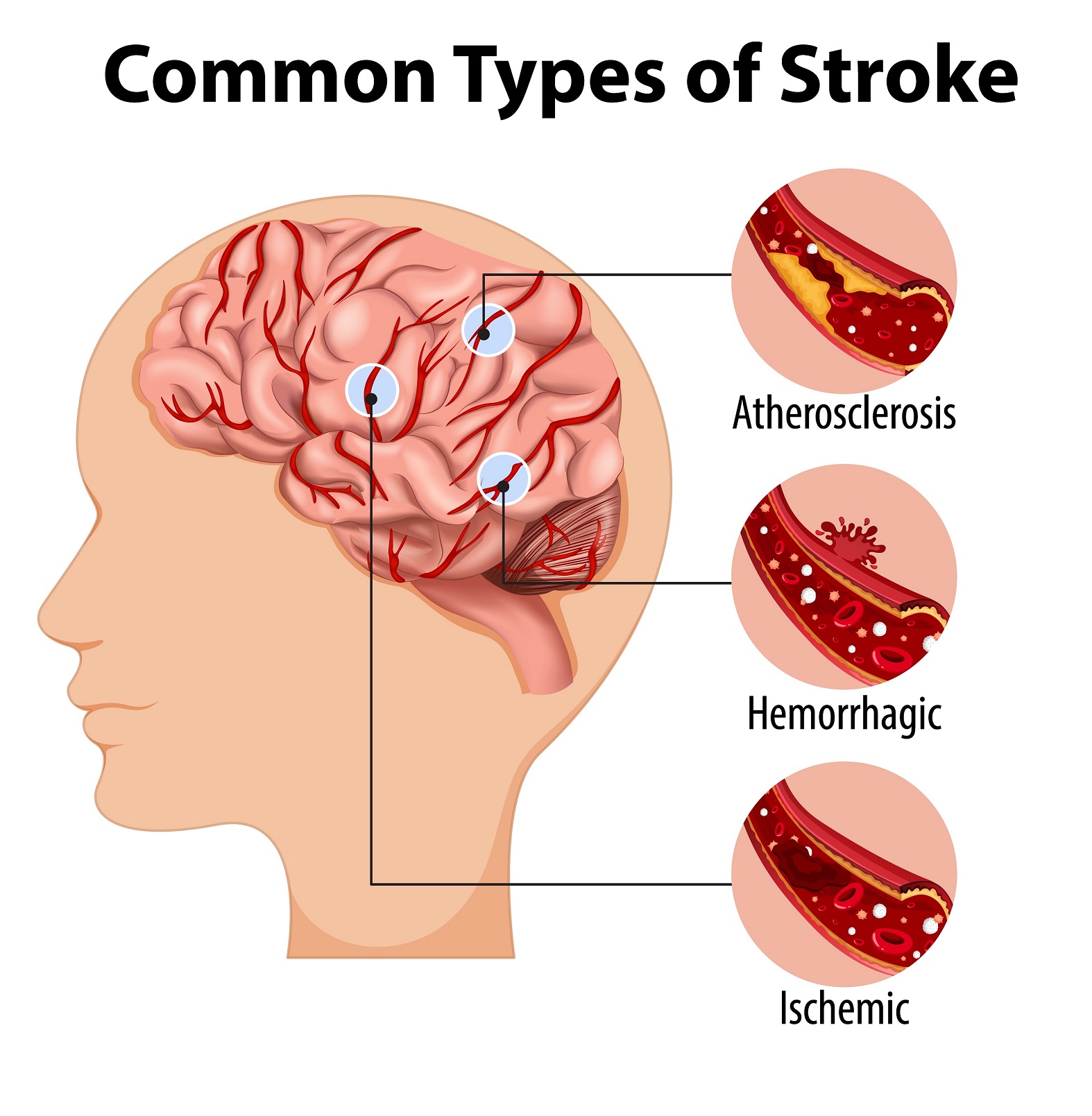
Heart disease is one of the greatest causes of premature death in Africa. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that the prevalence of hypertension is highest in the African region, with about 46 per cent of adults aged 25 years and older being hypertensive compared to 35 per cent in the Americas and other HIC and 40 per cent elsewhere in the world.
The HTT programme will be delivered through the company’s network of mutti pharmacies in Nigeria, Ghana, Kenya, and Zambia, with plans to expand the service to other countries.
The programme would aim to identify different classes of people, those at risk for hypertension, those who are about to develop hypertension and those who are already living with hypertension. The objectives would be to prevent, detect, and control the conditions.
Speaking at the launch of the programme in Nigeria, Dr Olagoke Ewedairo, VP of Health Services at mPharma, said the hypertension test and treat program is a service which aims to promote the early detection of hypertension, prompt treatment and prevention of complications such as hypertensive heart disease, kidney failure etc. which are on the rise despite being preventable.
The service includes a private consultation to review your medical history and current medications, determine your cardiovascular risk level and provide tailored lifestyle modification strategies to improve your health and wellbeing. In addition, a range of diagnostic tests would be available; all of these are to ensure you have a healthy heart.
On his part, Dr Hafeez Oluwa, the Global Primary Care Manager at mPharma, said that the company is taking a different approach to dealing with hypertension, going further than just helping people who have already developed the condition to identify people who are at risk of hypertension and collaborating with them to prevent the development of the disease.
“The passive approach has just led to numbers rising exponentially. We need to think more about primary prevention as we deal with hypertension with health promotion. If we start implementing lifestyle changes at an earlier stage, we may prevent more diagnoses of hypertension”, he said, speaking at the launch.
The programme has been rolled out in stages, the first stage was using the ongoing diabetes programme at mPharma, Diabetes Test and Treat, which has helped over 3000 patients achieve optimal glycemic control, become more aware of their risk of developing hypertension and helping those who have been diagnosed be more adherent to their medication.
The second stage was identifying people living with hypertension around our communities and deploying health education and coaching to help them control their blood pressure. Mr Dominic, a beneficiary of the program, said he was happy with the initiative as he got more insights into some of the things he had been doing that were preventing him from getting better. He wanted mPharma to do more to make sure many more people like him have access to this initiative.
The programme, in its final form, will include more people in its target audience, including people identified as being at risk of hypertension. It would be available in Kenya as a subscription service for purchase through mPharma mutti pharmacies and in subsequent months in other countries. It aligns with mPharma’s vision of providing accessible and affordable care to patients in vulnerable communities across Africa by transforming its mutti pharmacies into primary healthcare centres.
The hypertension test and treat service launches at select mutti pharmacies in Nigeria are effective today. Patients can visit any of mPharma mutti pharmacies to check their blood pressure for free and discuss their eligibility program.
mPharma plans to expand the hypertension test and treatment service to all 500 locations of mutti branches over time as the company’s ultimate aim is to put every African in good health and to contribute their quota to making universal healthcare coverage available to all.
Health
Oyo Seals Ar-Rahmon Khabul Herbal Over Health Concerns

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
An Ibadan-based herbal company, Ar-Rahmon Khabul Herbal Nigeria Limited, has been sealed by the Oyo State Rule of Law Enforcement Authority (OYRLEA).
The state government, in a statement signed on Friday by the Commissioner for Information, Mr Dotun Oyelade, revealed that the herbal firm was shut down due to environmental violations and public health concerns.
The leader of OYRLEA, Mrs Aderonke Aderemi, explained that the action was taken after multiple petitions from residents alleging persistent offensive odour and health challenges linked to the company’s operations.
She noted that the state government swung into action “to protect public health, preserve environmental standards, and enforce regulatory compliance across the state.”
It was gathered that investigations identified tobacco leaf as a major component in its production process, generating a strong, putrid odour deemed hazardous to residents and capable of posing serious health risks to the surrounding community.
“Joint inspections by officials revealed that the company operates a herbal production facility within a densely populated residential area, in clear violation of environmental and public health standards,” the statement said, adding that further findings from the inspection include the emission of harmful and toxic gaseous substances into the atmosphere, the discharge of wastewater into a nearby community water body, the installation of a chimney deemed too short and directly facing residential buildings, and the accumulation of solid waste within the premises despite claims of engaging a waste contractor, among others.
Prior to the enforcement action, the agency had issued an abatement notice directing the company to cease operations and relocate within 21 days in accordance with the Oyo State Environmental, Sanitation and Waste Control Regulations.
OYRLEA, along with the agencies that carried out the enforcement, reiterates that air pollution, hazardous waste discharge, and improper waste management are violations of environmental laws.
Mrs Aderemi reaffirmed OYRLEA’s commitment to sustained monitoring and enforcement to ensure a safe and healthy environment for all residents.
Health
NAFDAC Receives Seized Pharmaceutical Products from Rivers Customs

By Bon Peters
The Port Harcourt Area I Command of the Nigeria Customs Service (NCS) has handed over pharmaceutical products intercepted at the Omagwa International Airport recently to the National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC).
The spokesman for the command, Mr Barilule Aanee, an Assistant Superintendent of Customs 1, said in a statement that the items were given to NAFDAC on February 12, 2026, at the NAHCO Shed of the airport, where the seizure occurred.
The Customs Area Controller of the command, Comptroller Salamatu Atuluku, disclosed that the interception was made during routine examination and intelligence-driven scrutiny at the NAHCO Shed by officers of the Command in collaboration with relevant agencies.
She disclosed that six packages of pharmaceutical products, including Menotrophin 150 IU injections, Progesterone, and Isifrane, as well as three packages of medicaments containing Tramadol Ratiopharm injections, were discovered in two separate consignments.
The products, according to the statement, were neither properly declared nor accompanied by the mandatory NAFDAC certification required for lawful importation into Nigeria.
The Customs Area 1 chief further revealed that one shipment, originating under the name Zecho Oil and Gas Nigeria Limited for Elite Health Pharmacy Ltd, with Airway Bill No. 020 34858250, weighing 135 kilograms and amounting to 4,300 units, transported by Lufthansa Cargo Airline, was among the seized products.
More so, another consignment on Allied Airway Bill No. 574 34543283 from Amsterdam was falsely declared as spare parts.
She emphasised that regardless of the importer or volume involved, “no pharmaceutical product is permitted entry into Nigeria without proper declaration and regulatory clearance from NAFDAC.”
Comptroller Atuluku commended the diligence of the Customs Intelligence Unit and all officers involved, stressing that sustained interagency cooperation remained vital to strengthening enforcement and preserving the integrity of the nation’s supply chain.
While receiving the items, the Deputy Director of the NAFDAC Port Inspection Directorate, Pharm. Adepoju Bayo Raufu, thanked the customs for its vigilance and prompt handover of the intercepted items.
He assured that the agency would subject the items to appropriate regulatory procedures in line with its mandate to safeguard public health.
Health
Accurate Multi-Panel Drug Test Cups For Professionals

In safety-sensitive workplaces, clinical settings, and staffing operations, reliable on-site drug screening is a practical first line of defense. Accurate multi-panel drug test cups for professionals combine speed with portability, allowing organizations to screen for multiple substances quickly while preserving chain-of-custody and sample integrity. This guide explains how these cups work, how to choose the right product for a professional setting, and how to manage administration, interpretation, and compliance to reduce legal risk and costly false positives.
What Multi-Panel Drug Test Cups Are And Who Should Use Them
Multi-panel drug test cups are self-contained immunoassay devices that screen a urine sample for multiple drug classes simultaneously, typically including amphetamines, cocaine metabolites, opioids, cannabinoids (THC), benzodiazepines, and others depending on the panel. They are designed for point-of-care use: a donor provides a urine specimen directly into the cup, and the integrated test strips produce rapid visual results within minutes.
Who should use them? Professionals that benefit most include:
- Occupational health and human resources teams conducting pre-employment, post-incident, or random testing programs.
- Substance use clinicians and treatment centers performing routine monitoring.
- Staffing firms and temp agencies that need quick screening before placement.
- Corrections and probation officers performing supervision checks.
- Employers in transportation, construction, healthcare, and manufacturing where safety is critical.
For organizations prioritizing both speed and defensibility, multi-panel cups offer a pragmatic balance: they provide immediate screening to inform next steps while still allowing for confirmatory laboratory testing when required.
How Multi-Panel Test Cups Work: Technology And Accuracy Factors
At their core, most multi-panel cups use lateral flow immunoassay technology. Antibodies embedded on test strips bind to drug metabolites in the specimen: a visible line forms (or disappears) according to the assay design, indicating a negative or presumptive positive.
Key accuracy factors to understand:
- Antibody specificity and cross-reactivity: High-quality assays use antibodies selected to minimize cross-reactivity with over-the-counter medications or endogenous compounds. Lower-grade tests may yield false positives when donors take legal medications that share similar metabolites.
- Cutoff concentrations: Each assay has a cutoff (measured in ng/mL) that determines whether a result is reported as positive. Most professional cups follow SAMHSA or DOT cutoffs for workplace testing: knowing these thresholds reduces misinterpretation.
- Temperature and matrix checks: Modern cups often integrate temperature strips and creatinine/oxidant checks to detect dilution or tampering. These integrity features improve the reliability of on-site results.
- Operator influence: Proper collection, timing, and result reading windows directly affect accuracy. Even the best cup can produce incorrect readings if the test is read too early or too late.
Real-world accuracy is often expressed in sensitivity (ability to detect positives) and specificity (ability to rule out negatives). Professional cups from reputable manufacturers typically report >95% agreement with laboratory immunoassays at the stated cutoffs, though confirmatory GC-MS or LC-MS/MS remains the gold standard for legal or employment consequences.
Choosing The Right Cup For Professional Settings
Selecting the appropriate multi-panel drug test cup requires more than picking a high panel count. It’s about matching features to use case, workflow, and legal requirements.
Key Selection Criteria
- Regulatory alignment: Choose cups that adhere to SAMHSA/DOT cutoffs if testing falls under federal guidelines.
- Built-in integrity checks: Temperature, adulteration, and creatinine tests help detect tampering or dilution at collection.
- Ease of use: Simple, unambiguous results and clear timing windows reduce operator error and training burden.
- Documentation options: Cups that help clear labeling, lot tracking, and photo documentation streamline chain-of-custody.
- Shelf life and storage needs: Longer shelf life and uncomplicated storage conditions simplify inventory management.
Panel Selection: Which Drugs To Include
Common professional panels are 5-, 8-, or 12-panel cups. Decisions should be risk-based:
- 5-panel: Standard workplace screens (AMP, COC, OPI, THC, BZO).
- 8–12 panel: Add methamphetamine, oxycodone, fentanyl, barbiturates, PCP, and others where clinical or workplace exposure warrants it.
Staffing and healthcare employers often opt for expanded panels that include fentanyl and synthetic opioids given their prevalence.
Sensitivity, Cutoffs, And False Positives
Higher sensitivity isn’t always better: it may detect clinically irrelevant low levels or passive exposure. Professional programs typically use established cutoffs to balance sensitivity and specificity. When a presumptive positive appears, organizations must have a policy for confirmatory testing rather than making employment decisions on a single cup result.
Adulteration Detection And Integrity Features
Buy cups with built-in tamper indicators: temperature strips (correct collection window), creatinine or pH checks, and oxidant detection. These features lower the likelihood of undetected sample manipulation and strengthen the defensibility of the screening process.
Best Practices For Collection And Administration
Accurate results start with consistent collection procedures and well-trained staff.
Chain Of Custody And Documentation
Maintain an unbroken chain of custody: donor identification, time-stamped collection, witness signatures, and secure transport for confirmatory samples. Use standardized forms and consider photo documentation or barcode systems that tie cups to donor records. This reduces disputes and protects both employer and donor.
Proper Sample Collection And Handling Steps
- Verify donor identity and inspect the collection area for prohibited items.
- Instruct the donor to provide an adequate volume into the cup: record temperature immediately.
- Observe, where policy and law permit, to prevent substitution.
- Seal and label samples promptly if they will be sent for confirmatory testing.
- Adhere to manufacturers’ timing for reading results: most cups specify a 5–10 minute window.
Training Staff And Reducing Human Error
Regular staff training on procedure, result interpretation, and documentation reduces mistakes. Provide quick-reference guides, role-play common scenarios, and audit collections periodically to ensure compliance.
Interpreting Results And When To Confirm
On-site cups deliver presumptive results, actionable only within a clear policy framework.
Reading Immunoassay Results Correctly
Most cups use a two-line format: a control line indicating the test is valid, and a test line indicating a negative or positive depending on the device. A faint test line usually indicates a negative result at or above the cutoff: no test line indicates a presumptive positive. Staff should follow the manufacturer’s visual guide and timing strictly. Photographing results can help document ambiguous cases.
Confirmatory Testing: When And How To Send Samples
Any presumptive positive that could have employment consequences should be sent to a certified laboratory for confirmatory testing using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). It’s best practice to split or retain an aliquot during collection for immediate confirmatory shipment if required. Establish relationships with accredited labs and clarify reporting timeframes, cutoff standards, and evidence handling procedures.
Legal, Regulatory, And Privacy Considerations
Testing programs operate in a regulated and privacy-sensitive environment: mishandling can result in litigation or regulatory penalties.
Compliance With Workplace Testing Regulations
Understand federal, state, and industry-specific regulations that apply to the organization. Transportation and DOT-regulated employees face stricter protocols, specific cutoffs, and certified collector requirements. Non-DOT employers still should align policies with best practices to maintain defensibility.
Recordkeeping, Privacy, And Liability Best Practices
Limit access to test results to authorized personnel, store records securely, and retain documentation according to legal retention requirements. Clear written policies that explain testing rationale, disciplinary procedures, and the appeals process help mitigate liability. Include provisions for reasonable accommodations and medical review officers (MROs) who assess legitimate medical explanations for positive results.
Storage, Shelf Life, And Vendor Reliability
Purchasing decisions affect accuracy and supply-chain resilience.
Storage Conditions, Expiry, And Inventory Management
Store cups per manufacturer recommendations, usually at controlled room temperature away from direct sunlight. Track lot numbers and expiration dates in inventory systems and rotate stock using FIFO principles. Expired tests can degrade antibody performance and increase error rates.
Evaluating Suppliers And Quality Assurance Practices
Work with suppliers that provide lot-level COAs (Certificates of Analysis), recall notifications, and prompt customer support. Vet vendors for ISO or other quality certifications, clear warranty policies, and responsiveness to post-sale technical questions. For agencies that manage testing programs for clients, documented supplier reliability reduces operational risk and preserves client trust.
Conclusion
Accurate multi-panel drug test cups for professionals are a practical tool when used within a rigorously designed program: choose products that match regulatory requirements, incorporate integrity checks, and come from reliable vendors. Combine those choices with standardized collection procedures, trained staff, and clear confirmatory pathways to reduce false positives and legal exposure.
For agencies and businesses that support client organizations, whether staffing firms or occupational health providers, investing in the right cups and operational controls pays off in defensible screening results and smoother downstream workflows. When testing has real consequences, a presumptive result from a quality cup should be the beginning of a controlled process, not the final word.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn