Technology
The Ultimate Online Privacy Guide

By Douglas Crawford
Introduction
Edward Snowden’s NSA spying revelations highlighted just how much we have sacrificed to the gods of technology and convenience something we used to take for granted, and once considered a basic human right – our privacy.
It is just not just the NSA. Governments the world over are racing to introduce legislation that allows to them to monitor and store every email, phone call and Instant Message, every web page visited, webinar software and every VoIP conversation made by every single one of their citizens.
The press has bandied parallels with George Orwell’s dystopian world ruled by an all-seeing Big Brother about a great deal. They are depressingly accurate.
Encryption provides a highly effective way to protect your internet behavior, communications, and data. The main problem with using encryption is that its use flags you up to organizations such as the NSA for closer scrutiny.
Details of the NSA’s data collection rules are here. What it boils down to is that the NSA examines data from US citizens, then discards it if it’s found to be uninteresting. Encrypted data, on the other hand, is stored indefinitely until the NSA can decrypt it.
The NSA can keep all data relating to non-US citizens indefinitely, but practicality suggests that encrypted data gets special attention.
If a lot more people start to use encryption, then encrypted data will stand out less, and surveillance organizations’ job of invading everyone’s privacy will be much harder. Remember – anonymity is not a crime!
How Secure is Encryption?
Following revelations about the scale of the NSA’s deliberate assault on global encryption standards, confidence in encryption has taken a big dent. So let’s examine the current state of play…
Encryption Key Length
 Key length is the crudest way of determining how long a cipher will take to break. It is the raw number of ones and zeros used in a cipher. Similarly, the crudest form of attack on a cipher is known as a brute force attack (or exhaustive key search). This involves trying every possible combination to find the correct one.
Key length is the crudest way of determining how long a cipher will take to break. It is the raw number of ones and zeros used in a cipher. Similarly, the crudest form of attack on a cipher is known as a brute force attack (or exhaustive key search). This involves trying every possible combination to find the correct one.
If anyone is capable of breaking modern encryption ciphers it is the NSA, but to do so is a considerable challenge. For a brute force attack:
- A 128-bit key cipher has 3.4 x10(38) possible keys. Going through each of them would thousands of operations or more to break.
- In 2011 the fastest supercomputer in the word (the Fujitsu K computer located in Kobe, Japan) was capable of an Rmax peak speed of 10.51 petaflops. Based on this figure, it would take Fujitsu K 1.02 x 10(18) (around 1 billion) years to crack a 128-bit AES key by force.
- In 2016 the most powerful supercomputer in the world is the NUDT Tianhe-2 in Guangzhou, China. Almost 3 times as fast as the Fujitsu K, at 33.86 petaflops, it would “only” take it around a third of a billion years to crack a 128-bit AES key. That’s still a long time, and is the figure for breaking just one key.
- A 256-bit key would require 2(128) times more computational power to break than a 128-bit one.
- The number of years required to brute force a 256-bit cipher is 3.31 x 10(56) – which is about 20000….0000 (total 46 zeros) times the age of Universe (13.5 billion or 1.35 x 10(10) years!

128-bit Encryption
Until the Edward Snowden revelations, people assumed that 128-bit encryption was in practice uncrackable through brute force. They believed it would be so for around another 100 years (taking Moore’s Law into account).
In theory, this still holds true. However, the scale of resources that the NSA seems willing to throw at cracking encryption has shaken many experts’ faith in these predictions. Consequently, system administrators the world over are scrambling to upgrade cipher key lengths.
If and when quantum computing becomes available, all bets will be off. Quantum computers will be exponentially more powerful than any existing computer, and will make all current encryption ciphers and suites redundant overnight.
In theory, the development of quantum encryption will counter this problem. However, access to quantum computers will initially be the preserve of the most powerful and wealthy governments and corporations only. It is not in the interests of such organizations to democratize encryption.
For the time being, however, strong encryption is your friend.
Note that the US government uses 256-bit encryption to protect ‘sensitive’ data and 128-bit for ‘routine’ encryption needs.
However, the cipher it uses is AES. As I discuss below, this is not without problems.
Ciphers
Encryption key length refers to the amount of raw numbers involved. Ciphers are the mathematics used to perform the encryption. It is weaknesses in these algorithms, rather than in the key length, that often leads to encryption breaking.
By far the most common ciphers that you will likely encounter are those OpenVPN uses: Blowfish and AES. In addition to this, RSA is used to encrypt and decrypt a cipher’s keys. SHA-1 or SHA-2 are used as hash functions to authenticate the data.
AES is generally considered the most secure cipher for VPN use (and in general). Its adoption by the US government has increased its perceived reliability, and consequently its popularity. However, there is reason to believe this trust may be misplaced.
NIST
The United States National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) developed and/or certified AES, RSA, SHA-1 and SHA-2. NIST works closely with the NSA in the development of its ciphers.
Given the NSA’s systematic efforts to weaken or build backdoors into international encryption standards, there is every reason to question the integrity of NIST algorithms.
NIST has been quick to deny any wrongdoing (“NIST would not deliberately weaken a cryptographic standard”). It has also has invited public participation in a number of upcoming proposed encryption-related standards in a move designed to bolster public confidence.
The New York Times, however, has accused the NSA of introducing undetectable backdoors, or subverting the public development process to weaken the algorithms, thus circumventing NIST-approved encryption standards.
News that a NIST-certified cryptographic standard – the Dual Elliptic Curve algorithm (Dual_EC_DRGB) had been deliberately weakened not just once, but twice, by the NSA destroyed pretty much any existing trust.

That there might be a deliberate backdoor in Dual_EC_DRGB had already been noticed before. In 2006 researchers at the Eindhoven University of Technology in the Netherlands noted that an attack against it was easy enough to launch on ‘an ordinary PC.’ Microsoft engineers also flagged up a suspected backdoor in the algorithm.
Despite these concerns, where NIST leads, industry follows. Microsoft, Cisco, Symantec and RSA all include the algorithm in their products’ cryptographic libraries. This is in large partbecause compliance with NIST standards is a prerequisite to obtaining US government contracts.
NIST-certified cryptographic standards are pretty much ubiquitous worldwide throughout all areas of industry and business that rely on privacy (including the VPN industry). This is all rather chilling.
Perhaps because so much relies on these standards, cryptography experts have been unwilling to face up to the problem.
Perfect Forward Secrecy
One of the revelations in the information provided by Edward Snowden is that “another program, code-named Cheesy Name, was aimed at singling out SSL/TLS encryption keys, known as ‘certificates,’ that might be vulnerable to being cracked by GCHQ supercomputers.”
That these certificates can be “singled out” strongly suggests that 1024-bit RSA encryption (commonly used to protect the certificate keys) is weaker than previously thought. The NSA and GCHQ could therefore decrypt it much more quickly than expected.
In addition to this, the SHA-1 algorithm widely used to authenticate SSL/TLS connections is fundamentally broken. In both cases, the industry is scrambling fix the weaknesses as fast as it can. It is doing this by moving onto RSA-2048+, Diffie-Hellman, or Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) key exchanges and SHA-2+ hash authentication.
What these issues (and the 2014 Heartbleed Bug fiasco) clearly highlight is the importance of using perfect forward secrecy (PFS) for all SSL/TLS connections.
This is a system whereby a new and unique (with no additional keys derived from it) private encryption key is generated for each session. For this reason, it is also known as an ephemeral key exchange.
Using PFS, if one SSL key is compromised, this does not matter very much because new keys are generated for each connection. They are also often refreshed during connections. To meaningfully access communications these new keys would also need to be compromised. This makes the task so arduous as to be effectively impossible.
Unfortunately, it is common practice (because it’s easy) for companies to use just one private encryption key. If this key is compromised, then the attacker can access all communications encrypted with it.
OpenVPN and PFS
The most widely used VPN protocol is OpenVPN. It is considered very secure. One of the reasons for this is because it allows the use of ephemeral keys.
Sadly this is not implemented by many VPN providers. Without perfect forward secrecy, OpenVPN connections are not considered secure.
It is also worth mentioning here that the HMAC SHA-1 hashes routinely used to authenticate OpenVPN connections are not a weakness. This is because HMAC SHA-1 is much less vulnerable to collision attacks than standard SHA-1 hashes. Mathematical proof of this is available in this paper.
The Takeaway – So, is Encryption Secure?
To underestimate the NSA’s ambition or ability to compromise all encryption is a mistake. However, encryption remains the best defense we have against it (and others like it).
To the best of anyone’s knowledge, strong ciphers such as AES (despite misgivings about its NIST certification) and OpenVPN (with perfect forward secrecy) remain secure.
As Bruce Schneier, encryption specialist, fellow at Harvard’s Berkman Center for Internet and Society, and privacy advocate famously stated,
“Trust the math. Encryption is your friend. Use it well, and do your best to ensure that nothing can compromise it. That’s how you can remain secure even in the face of the NSA.”
Remember too that the NSA is not the only potential adversary. However, most criminals and even governments have nowhere near the NSA’s ability to circumvent encryption.
The Importance of End-to-end Encryption
End-to-end (e2e) encryption means that you encrypt data on your own device. Only you hold the encryption keys (unless you share them). Without these keys, an adversary will find it extremely difficult to decrypt your data.

Many services and products do not use e2e encryption. Instead they encrypt your data and hold the keys for you. This can be very convenient, as it allows for easy recovery of lost passwords, syncing across devices, and so forth. It does mean, however, that these third parties could be compelled to hand over your encryption keys.
A case in point is Microsoft. It encrypts all emails and files held in OneDrive (formerly SkyDrive), but it also holds the encryption keys. In 2013 it used these to unlock the emails and files of its 250 million worldwide users for inspection by the NSA.
Strongly avoid services that encrypt your data on their servers, rather than you encrypting your own data on your own machine.
HTTPS
Although strong encryption has recently become trendy, websites have been using strong end-to-end encryption for the last 20 years. After all, if websites were not secure, then online shopping or banking wouldn’t be possible.
The encryption protocol used for this is HTTPS, which stands for HTTP Secure (or HTTP over SSL/TLS). It is used for websites that need to secure users’ communications and is the backbone of internet security.
When you visit a non-secure HTTP website, data is transferred unencrypted. This means anyone watching can see everything you do while visiting that site. This includes your transaction details when making payments. It is even possible to alter the data transferred between you and the web server.
With HTTPS, a cryptographic key exchange occurs when you first connect to the website. All subsequent actions on the website are encrypted, and thus hidden from prying eyes. Anyone watching can see that you have visited a certain website, but cannot see which individual pages you read, or any data transferred.
For example, the BestVPN.com website is secured using HTTPS. Unless you are using a VPN while reading this web page, your ISP can see that you have visited www.bestvpn.com, but cannot see that you are reading this particular article. HTTPS uses end-to-end encryption.
It is easy to tell if you visit a website secured by HTTPS – just look for a locked padlock icon to the left of the main URL/search bar.
There are issues relating to HTTPS, but in general it is secure. If it wasn’t, none of the billions of financial transactions and transfers of personal data that happen every day on the internet would be possible. The internet itself (and possibly the world economy!) would collapse overnight.
For a detailed discussion on HTTPS, please see here.
Metadata
An important limitation to encryption is that it does not necessarily protect users from the collection of metadata.
Even if the contents of emails, voice conversations, or web browsing sessions cannot be readily listened in on, knowing when, where, from whom, to whom, and how regularly such communication takes place can tell an adversary a great deal. This is a powerful tool in the wrong hands.
For example, even if you use a securely encrypted messaging service such as WhatsApp, Facebook will still be able to tell who you are messaging, how often you message, how long you usually chat for, and more. With such information, it would be easy to discover that you were having an affair, for example.
Although the NSA does target individual communications, its primary concern is the collection of metadata. As NSA General Counsel Stewart Baker has openly acknowledged,
“Metadata absolutely tells you everything about somebody’s life. If you have enough metadata, you don’t really need content.“
Technologies such as VPNs and Tor can make the collection of metadata very difficult. For example, an ISP cannot collect metadata relating to the browsing history of customers who use a VPN to hide their online activities.
Note, though, that many VPN providers themselves log some metadata. This should be a consideration when choosing a service to protect your privacy.
Please also note that mobile apps typically bypass any VPN that is running on your device, and connect directly to their publishers’ servers. Using a VPN, for example, will not prevent WhatsApp sending metadata to Facebook.
Identify Your Threat Model
When considering how to protect your privacy and stay secure on the internet, carefully consider who or what worries you most. Defending yourself against everything is almost impossible. And any attempt to do so will likely seriously degrade the usability (and your enjoyment) of the internet.
Identifying to yourself that being caught downloading an illicit copy of Game of Thrones is a bigger worry than being targeted by a crack NSA TAO teamfor personalized surveillance is a good start. It will leave you less stressed, with a more useable internet and with more effective defenses against the threats that really matter to you.
Of course, if your name is Edward Snowden, then TAO teams will be part of your threat model…
I will discuss steps you should take to help identify your threat model in an upcoming article on BestVPN.com. In the meantime, this article does a good job of introducing the basics.
Use FOSS Software
 The terrifying scale of the NSA’s attack on public cryptography, and its deliberate weakening of common international encryption standards, has demonstrated that no proprietary software can be trusted. Even software specifically designed with security in mind.
The terrifying scale of the NSA’s attack on public cryptography, and its deliberate weakening of common international encryption standards, has demonstrated that no proprietary software can be trusted. Even software specifically designed with security in mind.
The NSA has co-opted or coerced hundreds of technology companies into building backdoors into their programs, or otherwise weakening security in order to allow it access. US and UK companies are particularly suspect, although the reports make it clear that companies across the world have acceded to NSA demands.
The problem with proprietary software is that the NSA can fairly easily approach and convince the sole developers and owners to play ball. In addition to this, their source code is kept secret. This makes it easy to add to or modify the code in dodgy ways without anyone noticing.

The best answer to this problem is to use free open source software (FOSS). Often jointly developed by disparate and otherwise unconnected individuals, the source code is available to everyone to examine and peer-review. This minimizes the chances that someone has tampered with it.
Ideally, this code should also be compatible with other implementations, in orderto minimize the possibility of a backdoor being built in.
It is, of course, possible that NSA agents have infiltrated open source development groups and introduced malicious code without anyone’s knowledge. In addition, the sheer amount of code that many projects involve means that it is often impossible to fully peer-review all of it.
Despite these potential pitfalls, FOSS remains the most reliable and least likely to be tampered with software available. If you truly care about privacy you should try to use it exclusively (up to and including using FOSS operating systems such as Linux).
Steps You Can Take to Improve Your Privacy
With the proviso that nothing is perfect, and if “they” really want to get you “they” probably can, there are steps you can take to improve your privacy.
Pay for Stuff Anonymously
One step to improving your privacy is to pay for things anonymously. When it comes to physical goods delivered to an actual address, this isn’t going to happen. Online services are a different kettle of fish, however.
It is increasingly common to find services that accept payment through Bitcoin and the like. A few, such as VPN service Mullvad, will even accept cash sent anonymously by post.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a decentralized and open source virtual currency that operates using peer-to-peer technology (much as BitTorrent and Skype do). The concept is particularly revolutionary and exciting because it does not require a middleman to work (for example a state-controlled bank).
Whether or not Bitcoins represent a good investment opportunity remains hotly debated, and is not within the remit of this guide. It is also completely outside of my area of expertise!
Source: Bestvpn.com
Technology
Truecaller, AnyMind Group to Expand Direct Sales Footprint

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The leading global communications platform, Truecaller, now has a strategic direct sales reseller partnership with AnyMind Group, a Business-Process-as-a-Service company for marketing, e-commerce and digital transformation.
Under this partnership, AnyMind Group will serve as the exclusive intermediary for Truecaller’s advertising inventory across Egypt, UAE, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Israel, Ghana, Nigeria, Morocco, Malaysia, Singapore and Vietnam.
The scope of the partnership is focused specifically on enabling brands and agencies to leverage Truecaller’s premium ad formats to reach highly engaged, high-intent users through relevant, data-driven advertising solutions.
Through this collaboration, Truecaller will accelerate its direct advertising business across the Middle East & North Africa (MENA) and Southeast Asia (SEA) regions.
With a strong on-ground presence and established relationships with leading advertisers and agencies across MENA and SEA markets, AnyMind Group brings deep regional expertise that will support the scaling of Truecaller’s advertising footprint locally.
The partnership is designed to empower brands with impactful placements on Truecaller’s trusted communications platform, helping drive meaningful engagement with users in these fast-growing digital economies.
“As Truecaller continues to expand its global advertising business, partnerships with strong regional players like AnyMind Group are critical to delivering localised expertise and measurable outcomes for advertisers.
“MENA and Southeast Asia represent high-growth markets with evolving digital maturity, and through this collaboration, we aim to bring brands closer to consumers via trusted and contextual communication experiences on our platform,” the Vice President and Global Head for Truecaller Ads Business, Hemant Arora, said.
Also, the Managing Director for Growth Markets at AnyMind Group, Aditya Aima, said, “We are excited to partner with Truecaller to open its inventory to brands across MENA and Southeast Asia. With Truecaller’s scale and trusted user ecosystem, combined with our market depth and networks, we see strong potential to drive more relevant, high-impact advertising outcomes for advertisers looking to deepen engagement in these dynamic markets.”
Technology
Capillary Technologies Acquires SessionM from Mastercard

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
A software product company established in 2012, Capillary Technologies India Limited, has acquired the customer engagement and loyalty company, SessionM, from Mastercard.
This followed a definitive agreement signed by the global leader in AI-powered customer loyalty and engagement solutions with the renowned digital payments firm.
The acquisition of SessionM is the latest in a series of strategic moves by Capillary, following its successful listing on the Indian Stock Exchange in November 2025.
With SessionM in its portfolio, Capillary reinforces its position as a global leader in enterprise loyalty, offering a leading platform to the world’s most sophisticated enterprise brands.
Mastercard has identified Capillary Technologies—consistently recognised as a Leader in The Forrester Wave as the ideal partner to lead SessionM into its next era of growth.
As part of the agreement, a specialised team within SessionM will transition to Capillary, ensuring that the platform’s deep technical expertise is preserved.
SessionM’s esteemed global customer base—which includes Fortune 500 retailers, airlines, and CPG brands—will continue to receive the same high-calibre support and service they experienced before the acquisition.
“M&A has been a key growth strategy for Capillary over the years, and as a public company, we are delivering on that promise to our shareholders and the market.
“By bringing SessionM into our portfolio, we are not just expanding our footprint across the globe; we are further strengthening our loyalty capabilities to deliver one of the industry’s most comprehensive offerings.
“Our mission remains to provide enterprises across industries with specialised, AI-native loyalty technology solutions,” the chief executive of Capillary Technologies, Aneesh Reddy, commented.
Technology
Emergent Ventures, Others Invest $2.2m in Potpie
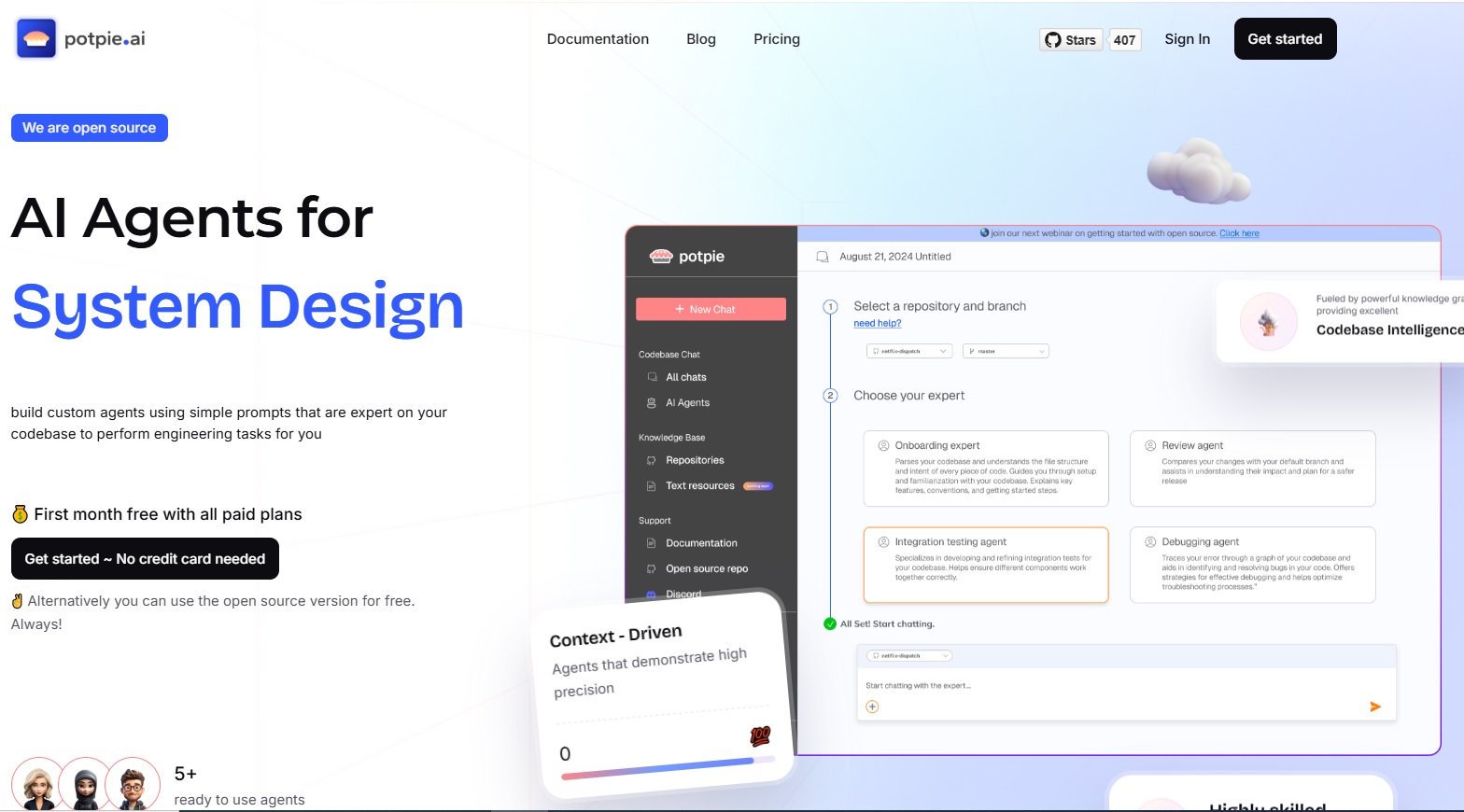
By Dipo Olowookere
About $2.2 million pre-seed round to help engineering teams unify context across their entire stack and make AI agents genuinely useful in complex software environments has been announced by Potpie.
Potpie was established by Aditi Kothari and Dhiren Mathur, who were determined to unify context across the entire engineering stack and enabling spec driven development.
As generative AI adoption accelerates, most tools focus on surface-level code generation while ignoring the deeper problem of context.
Large language models are powerful, but without access to system-level understanding, tooling history, and architectural intent, they struggle in real production environments.
Traditional approaches rely on senior engineers to manually hold this context together, a model that breaks down at scale and fails when AI agents are introduced.
The platform enables teams to automate high-impact and non-trivial use cases across the software development lifecycle, like debugging cross-service failures, maintaining and writing end-to-end tests, blast radius detection and system design.
It is designed for enterprise companies with large and complex codebases, starting at around one million lines of code and scaling to hundreds of millions.
Rather than acting as another coding assistant, Potpie builds a graphical representation of software systems, infers behaviour and patterns across modules, and creates structured artefacts that allow agents to operate consistently and safely.
A statement made available to Business Post on Monday revealed that the funding support came from Emergent Ventures, All In Capital, DeVC and Point One Capital.
The capital will be used to support early enterprise deployments, expand the engineering team, and continue building Potpie’s core context and agent infrastructure, it was disclosed.
“As AI makes code generation easier, the real challenge shifts to reasoning across massive, interconnected systems. Potpie is our answer to that shift, an ontology-first layer that helps enterprises truly understand and manage their software,” Kothari was quoted as saying in the disclosure.
A Managing Partner at Emergent Ventures, Anupam Rastogi, said, “In large enterprises, the real challenge is not generating code, it is understanding the system deeply enough to change it safely.
“Potpie’s ontology-first architecture, combined with rigorous context curation and spec-driven development, creates a structured model of the entire engineering ecosystem. This allows AI agents to reason across services, dependencies, tickets, and production signals with the clarity of a senior engineer. That is what makes Potpie uniquely capable of solving complex RCA, impact analysis, and high-risk feature work even in codebases exceeding 50 million lines.”
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn













1 Comment