Technology
Top Cybersecurity Projects

Introduction
Cybersecurity projects are a great way to learn more about the field and build your portfolio. They can also be fun, challenging, and rewarding—especially when you get to see what you made in action! In this article, we’ll go over some of our favorite cybersecurity projects that will help you start your journey into the industry.
The ethical hacker course from Knowledgehut will help you learn about the latest commercial-grade hacking tools, techniques, and methodologies. Pursue the course to develop cutting-edge skills and explore proven techniques and best practices to begin your career in ethical hacking.
Important Cybersecurity Projects
Some of the important cybersecurity projects are discussed below:
NetSecFocus
NetSecFocus is a community-driven cybersecurity project created as a collection of tools and resources for network security professionals. It uses open-source software where possible, with licensed content available under various licenses. The project is open to contributions from anyone interested in improving the platform by adding new features or reporting bugs.
As a GitHub repository, NetSecFocus provides source code that can be used to build your copy of the site (or just browse it online). The website is hosted using GitHub Pages to promote collaboration by making it easy for any contributor to update content on their computer before pushing changes back into central repositories shared with other contributors.
Kali Linux
Linux distribution Kali Linux was designed to be used for digital forensics and penetration testing, and it is derived from Debian. In addition to Kali Linux, Offensive Security Ltd. also develops commercial counterparts such as BlackArch and BackBox to address security concerns. It is based on Debian’s testing branch, yet at the time of writing, it was updated every three months.
The development team aims to not only provide new features but also fix bugs that they’re aware of or reported through bug trackers in each update release. Kali recently changed its name from BackTrack; both names are being used interchangeably within this article because they essentially refer to the same thing: an OS distribution with lots of hacking tools preinstalled (for example, Metasploit).
Capsule8
Capsule8 is a cloud-based security platform that provides visibility into and protection against threats in the data center. The platform enables you to protect containers, applications, and infrastructure with automatic threat detection, vulnerability scanning, and continuous monitoring of your entire containerized environment. Capsule8 can also monitor your existing Kubernetes clusters, providing security for both new and existing deployments.
Capsule8 provides a single pane of glass for security across your entire infrastructure. Capsule8’s container-native platform enables you to automatically detect and respond to threats in real time, including vulnerabilities, malware, and data breaches. You can also use Capsule8 to continuously monitor your environment for signs of compromise and remediate issues before they become serious problems.
Metasploit Framework
The Metasploit Framework is a tool that helps you find and exploit security vulnerabilities in networks. It is a framework that security professionals, penetration testers, and hackers can use. HD Moore created the Metasploit Framework in 2003 to help automate tasks for network administrators and security consultants, but it has since been expanded to include a huge community that contributes code and new modules all the time.
The Metasploit Framework allows you to write your scripts, called modules. These can be used to perform a wide range of tasks, from scanning for vulnerabilities in a network to exploiting those vulnerabilities and gaining access. The software also comes with a database of pre-written tools that can be used right away.
SUBgraph OS
SUBgraph OS is a Linux-based operating system designed to be resistant to cyberattacks. It was developed by a team of security researchers, who are also the founders of SUBnet Labs, which developed SUBgraph OS as part of their research into information security. The developers describe SUBgraph as “a privacy-focused operating system” protected by “hosted virtualization” and an “isolated hypervisor.”
It means that while it’s based on the Linux kernel like other operating systems (such as Ubuntu), it doesn’t share any code with those other systems. It uses virtualization to create an isolated container where dangerous processes cannot access your data on the hard drive.
Google Grr
Google Grr is a collection of tools that help you detect and respond to advanced threats. The project was released in May 2018 by Google and MITRE with the intent to make the GRR tool available for Linux users.
The open-source GRR project (Github Repo) was created by Maxime Villard and inspired by an idea proposed by John Ellis during a talk at Defcon 2017 titled “Mountain Peak Performance: Achieving Enterprise Security at Scale.”
GRR is an open-source project that aims to provide a secure and reliable environment for anyone who uses Linux in their daily work. GRR is intended to be a complete solution that provides a secure and reliable environment while still being easy to use.
OpenCanary
OpenCanary is a free, open-source application security testing platform. It integrates with the Kubernetes API and the Prometheus monitoring system. OpenCanary can test applications for common vulnerabilities and misconfigurations by generating alerts if it detects something unusual happening in your application. In addition to its native runtime environment, OpenCanary supports other environments such as Slack, GCP Cloud Pub/Sub, AWS Lambda & Zappa.
The ethical hacker course will help you master the five steps of ethical hacking, including reconnaissance, gaining access, enumeration, maintaining access, and covering your tracks.
Cybersecurity projects to learn
- NetSecFocus: A security training platform that teaches cybersecurity basics, so you can dive deeper into specific areas of interest.
- Kali Linux: A Linux distribution used for penetration testing and security auditing because it contains hundreds of tools specifically designed for hacking, cracking, and information security research.
- Capsule8: An agentless network security platform that provides real-time visibility into threats across applications and infrastructure devices to enable an adaptive response to attacks.
- Metasploit Framework: An open-source framework used by many hackers for penetration testing purposes or simply checking whether their system has any vulnerabilities before being exploited by malicious actors online (or even by themselves).
- SUBgraph OS: A secure operating system designed from the ground up using various open-source tools focused on privacy protection, including support for hardware-based memory encryption (Intel SGX).
Conclusion
There are many cybersecurity projects that can be carried out by a team of professionals. In conclusion, many different types of cybersecurity projects can be undertaken in your organization to ensure safety from cyberattacks and other threats. The best part about these solutions is that they can be implemented without any hassles or complications at all. Opt for the ethical hacker course offered by Knowledgehut and learn ethical hacking from scratch with the comprehensive course material to become a skilled ethical hacker.
FAQs
Q1. What are current trending topics in cybersecurity?
Ans. Photos, financial transactions, emails, and texts have more potential for posing a threat to individuals than they have ever been before. Viruses or malware installed on smartphones may be one of the trends that capture the attention of cybersecurity experts in 2023.
Q2. Which country is best in cybersecurity?
Ans. Three countries have the greatest capability when it comes to cyber surveillance: China, the United States, and Russia.
Q3. What are the most common cyber-attacks in 2022?
Ans. According to an analysis of attack vectors, credential theft remains the most common attack vector, followed by phishing, misconfigured clouds, and third-party vulnerabilities. When considering how long it takes to detect and contain each type of compromise, it becomes clear how important it is to prevent these attacks.
Q4. What is the largest hack in history?
Ans. In terms of cost and destructiveness, it is considered the biggest hack in history. This attack was apparently carried out by an Iranian attack group known as the cutting sword of justice. Iranian hackers retaliated against Stuxnet with the release of Shamoon. Saudi Aramco was impacted for months by the malware, which destroyed more than 35,000 computers.
Technology
Interswitch Technovation 4.0 Hackathon Winners Share N10m

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
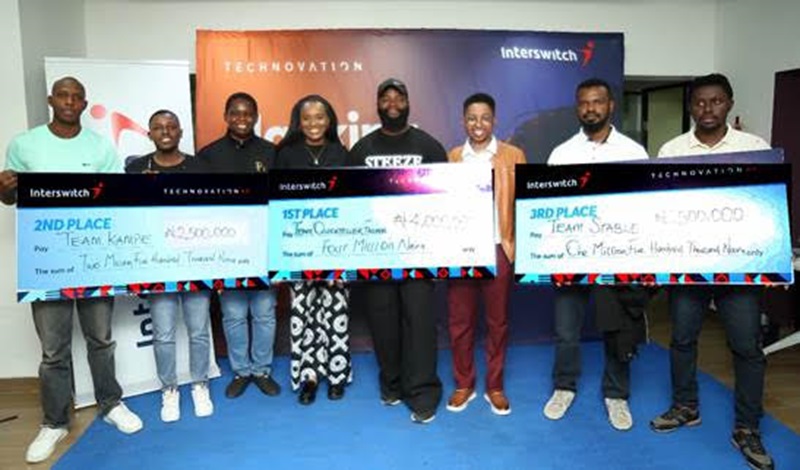
The winners of the Technovation 4.0 Hackathon, themed The Wicked Hackathon, organised by Interswitch, have been given N10 million in cash prizes for their efforts.
At the one-day finale event, which took place on Wednesday, March 4, 2026, at the Interswitch Innovation Lab and Co-Working Space, the money was shared among the top teams whose innovative solutions stood out during the rigorous multiple phases of the competition.
Team Quickteller Fashion emerged as the overall winner, securing the grand prize of N4 million for a solution that impressed judges with its originality, practicality, and strong strategic relevance. Team Kampe claimed second position with N2.5 million, while Team Stable placed third, receiving N1.5 million. Up to N300,000 worth of cash prizes were also awarded to the fourth, fifth and sixth qualifying teams.
For nine months, cross-functional teams from across the organisation collaborated to conceptualise, validate, develop, and refine solutions, moving from raw ideas to minimum viable products (MVPs) with ready-to-market potential and deployment across the business.
The atmosphere at the grand finale reflected that of preparation and anticipation as the top 9 teams presented their innovations through live demonstrations and detailed pitches, fielding questions from a distinguished panel of judges before the top three winners were selected. Each presentation highlighted rigorous validation processes, thoughtful market considerations, and a strong emphasis on measurable impact.
While many of the solutions remain confidential due to their strategic relevance, the diversity and depth of ideas showcased during the hackathon’s final underscored the organisation’s growing culture of intrapreneurship and structured innovation. The projects illustrated how technology-driven thinking can unlock efficiencies, strengthen operational capabilities, and open new pathways for growth across the digital payments and commerce ecosystem.
“Technovation continues to reflect who we are as an organisation, bold, forward-thinking, and deeply committed to building impactful solutions from within. Over the years, we have seen ideas conceived during this programme evolve into meaningful capabilities that strengthen our ecosystem.
“The passion, discipline, and ingenuity demonstrated by our teams this year reinforce our belief in the power of African innovation to solve complex challenges and shape the future of technology on the continent,” the Chief Innovation Officer for Interswitch, Ms Adaobi Okerekeocha, stated.
Technology
Google Introduces Yorùbá, Hausa Language Support for AI Search Features
By Modupe Gbadeyanka
The language support for its AI Search features has been expanded by Google, with the inclusion of Yoruba and Hausa in Nigeria.
This is part of a broader effort to make AI more inclusive across the continent, with support now extending to a total of 13 African languages.
Under the AI Overviews and AI Mode, speakers of both Nigerian languages can utilise AI-powered Search experiences in their mother tongue for quick summaries and conversational exploration.
This means existing AI features in Google Search are now accessible to people like the student in Kano asking a question in Hausa, and the trader in Ibadan seeking advice in Yorùbá.
By addressing language barriers, this update ensures that technology reflects the identity and culture of the people it serves. With this expansion, more people can now use AI Mode to ask complex questions in their preferred language, while exploring the web more deeply and naturally through text or voice.
The 13 languages now supported across Africa include Afrikaans, Akan, Amharic, Hausa, Kinyarwanda, Afaan Oromoo, Somali, Sesotho, Kiswahili, Setswana, Wolof, Yorùbá, and isiZulu.
These languages were chosen based on the vibrant search activity across the continent, ensuring that our AI experiences reach the communities that need them most.
Commenting on the development, the Communications and Public Affairs Manager for Google in West Africa, Taiwo Kola-Ogunlade, said, “Building a truly global Search goes far beyond translation — it requires a nuanced understanding of local information.
“With the advanced multimodal and reasoning capabilities of our custom version of Gemini in Search, we’ve made huge strides in language understanding, so our most advanced AI search capabilities are locally relevant and useful in each new language we support.
“This is about ensuring Nigerians can converse with Search in their mother tongues, making information more helpful for everyone.”
To use AI Overviews and AI Mode in the local language, users must open the Google app on an Android or iOS device, or via the Web. They are required to tap on AI Mode within the Search experience. Thereafter, they can type or speak the question in their preferred language, such as Hausa or Yorùbá, and let the AI guide the journey.
Technology
Telecom Operators to Issue 14-Day Notice Before SIM Disconnection

By Adedapo Adesanya
Telecommunications operators in Nigeria will now be required to give subscribers a minimum of 14 days’ notice before deactivating their SIM cards over inactivity or post-paid churn, following a fresh proposal by the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC).
The proposal is contained in a consultation paper, signed by the Executive Vice Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of the NCC, Mr Aminu Maida, and titled Stakeholders Consultation Process for the Telecoms Identity Risks Management Platform, dated February 26, 2026, and published on the Commission’s website.
Under the proposed amendments to the Quality-of-Service (QoS) Business Rules, the Commission said operators must notify affected subscribers ahead of any planned churn.
“Prior to churning of a post-paid line, the Operator shall send a notification to the affected subscriber through an alternative line or an email on the pending churning of his line,” the document stated.
It added that “this notification shall be sent at least 14 days before the final date for the churn of the number.”
A similar provision was proposed for prepaid subscribers. According to the Commission, operators must equally notify prepaid customers via an alternative line or email at least 14 days before the final churn date.
Currently, under Section 2.3.1 of the QoS Business Rules, a subscriber’s line may be deactivated if it has not been used for six months for a revenue-generating event. If the inactivity persists for another six months, the subscriber risks losing the number entirely, except in cases of proven network-related faults.
The new proposal is part of a broader regulatory review tied to the rollout of the Telecoms Identity Risk Management System (TIRMS), a cross-sector platform designed to curb fraud linked to recycled, swapped and barred mobile numbers.
The NCC explained in the background section of the paper that TIRMS is a secure, regulatory-backed platform that helps prevent fraud stemming from churned, swapped, barred Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Numbers in Nigeria.
It said this platform will provide a uniform approach for all sectors in relation to the integrity and utilisation of registered MSISDNs on the Nigerian Communications network.
In addition to the 14-day notice requirement, the Commission also proposed that operators must submit details of all churned numbers to TIRMS within seven days of completing the churn process, strengthening oversight and accountability in the system.
The consultation process, which the Commission said is in line with Section 58 of the Nigerian Communications Act 2003, will remain open for 21 days from the date of publication. Stakeholders are expected to submit their comments on or before March 20, 2026.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn






















1 Comment