Economy
API Architecture: The Invisible Engine Powering Modern Banking

By Echezona Agubata
Banking has evolved far beyond the days of paper ledgers and long queues. Today, it’s a dynamic force driving Nigeria’s economy, responding to customers in real time, and powering digital innovation. The unsung hero behind this transformation is the Application Programming Interface (API)—a tool that lets bank systems communicate seamlessly with each other and external partners.
In Nigeria’s fast-growing digital finance landscape, APIs are the invisible engine enabling banks to offer instant balance checks, process payments at retail checkouts, or verify identities for loan approvals. The secret to their success? A robust API architecture, the structured framework that makes banking secure, scalable, and innovative.
Picture API architecture as a bridge connecting islands of financial services. It allows banks to share data securely. In Nigeria, where digital banking is literarily booming, APIs let banks like Coronation Merchant Bank expand services without rebuilding infrastructure. This flexibility fuels innovation, enabling tailored solutions for everyone from small businesses to large corporations.
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) along with Industry players ensure this ecosystem is secure and trustworthy. Its regulations mandate standards like OAuth 2.0 for authentication, tokenization to protect data, and encrypted channels to safeguard transactions. Real-time monitoring and customer consent protocols further build trust, ensuring data is shared only with permission. These rules aren’t just technical or ethical—they’re the backbone of Nigeria’s open banking system, fostering collaboration and innovation.
How do APIs work? Imagine a well-orchestrated machine. The API acts as
● A Gateway: the gatekeeper to a product. It authenticates requests and ensures only authorized people are granted access to the product. It also helps limit the number of requests that can be made for the product at any given time. For instance, when a bank’s mobile app requests a customer’s transaction history, the transaction history API (as a gateway) verifies access (both customer and mobile app) before treating the transaction history request.
- A Guide: the protocol or security who ensures that even authenticated users are only allowed to access products and data that they are authorized to have
- A Funnell: the pipe that ensures that authenticated users access products and data from known locations/sources to known destinations
- An Agent: the agent that ensures that applications regardless of the service offering have access to data/products in the same way as every other application. This gives unified experience across respective platforms that are consuming the service/data offered by the API
Here’s a simplified view of the flow:
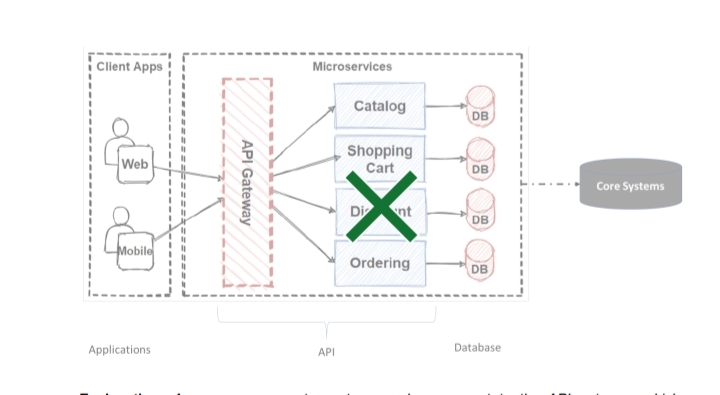
Explanation: An app or corporate system sends a request to the API gateway, which authenticates and routes it. The orchestration layer processes it using endpoints, pulling data from the core system via middleware.
The orchestration layer (behind the gateway) breaks services—like catalog, shopping cart, or ordering—into modular endpoints, like building blocks online shops can share securely. The modular endpoints connect these APIs to core systems, translating the requests into formats that can be processed by the core system. Companies also provide developer portals with clear documentation and sandbox environments, simplifying integration for partners.
This architecture can be built for scale. Banks process millions of transactions daily using load balancing to scale out resources, and distribute traffic in a dynamic fashion. This architecture could incorporate the use of in-memory databases and Queueing technologies to cache frequently used data for swifter processing. More so, this introduces rate limiting features which help isolate any problem areas without affecting the entire service as a whole.
Challenges abound. One of such is the existence of legacy systems as many banks and organizations often rely on decades-old mainframes (core systems), thus requiring a middleware solution to bridge old and new systems—a complex but critical step. Another recent challenge is the need to enforce data privacy expectations, this has made encryption and data masking a necessary action. Encryption in itself comes with its own attendant side-effects especially where applied on data without proper service governance. It can slow performance, so banks and organizations use caching and optimized data flows to balance speed and security. Compliance with CBN guidelines and Nigeria’s data privacy laws demands robust
consent management and audit trails. Versioning APIs (e.g., /v1/payments) prevents disruptions when systems evolve.
Real-world examples highlight APIs’ impact. Coronation Merchant Bank built the Dangote ISOP Collection API to streamline payments for Dangote’s distributors. These payments were previously riddled with slow reconciliations and delayed cash flow. The API integrates payments directly into Dangote’s ERP system and thereby automating the process, reducing errors, and strengthening business ties. Another bank used a KYC API to verify customer identities for loan applications, cutting onboarding time while meeting CBN standards. A third example involves a major Nigerian bank’s payment API, which enables instant corporate transfers for retailers, ensuring funds clear in seconds during peak sales.
APIs are also driving open finance. The CBN’s 2023 guidelines expand APIs to cover credit, investment, and insurance data, enabling embedded finance—loans at retail checkouts or savings tools linked to salary accounts. This makes banking invisible yet ever-present, blending into daily life.
The future is exciting. Banks are adopting API-first design, prioritizing APIs as core interfaces for faster innovation. AI-driven APIs are emerging, enabling fraud detection or tailored loan offers. Blockchain-based APIs promise secure cross-border payments. Event-driven architectures, using tools like Kafka, process real-time events like transaction alerts, boosting efficiency.
At Coronation Merchant Bank, our APIs are business enablers. Our custom solutions, like the Dangote integration, solve real-world problems, while our investment banking desk advises on capital raising and partnerships, helping clients stay competitive. APIs lower barriers, drive growth, and deliver seamless experiences for customers.
Nigeria’s financial future isn’t about who holds the most assets—it’s about who builds the strongest connections between data, money, and people. API architecture is the invisible engine powering that future, creating a connected, inclusive banking ecosystem.
Economy
NCSP, NACCIMA Move to Unlock SME-led Industrial Growth

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Nigeria–China Strategic Partnership (NCSP) has reaffirmed its commitment to consolidate engagements with the Organised Private Sector while strengthening strategic collaboration to accelerate Nigeria’s industrial expansion, following a high-level meeting with the leadership of the Nigerian Association of Chambers of Commerce, Industry, Mines and Agriculture (NACCIMA).
The dialogue focused on aligning institutional efforts to deepen Nigeria–China economic cooperation and position Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) as primary beneficiaries of trade, manufacturing, and investment initiatives.
The Director-General of NCSP, Mr Joseph Tegbe, stated that the Partnership was established as a structured coordination platform to drive Nigeria’s strategic economic engagement with China in a disciplined and result-oriented manner.
He outlined its core mandates, including oversight of FOCAC-related initiatives, advancement of priority economic initiatives, and the facilitation of catalytic industrial projects across priority sectors.
Mr Tegbe emphasised that the next phase of engagement will prioritize harmonization of ongoing initiatives, stronger inter-agency coordination, and clearer execution frameworks to ensure Nigerian businesses, particularly SMEs, benefit more directly and sustainably from bilateral trade and investment initiatives.
According to a statement, NSCP said the meeting reviewed existing collaborations and investment pipelines, with both parties agreeing on the need to streamline coordination across federal and subnational levels to improve policy coherence, enhance implementation efficiency and eliminate fragmentation to take advantage of scale.
Mr Tegbe further highlighted the strategic importance of leveraging landmark trade instruments like China’s Zero-Tariff Agreement with African countries as a pathway to scale-up domestic manufacturing, deepen value addition, and strengthen Nigeria’s export competitiveness.
On his part, the President of NACCIMA and Chairman of the Organised Private Sector of Nigeria (OPSN), Mr Jani Ibrahim, commended NCSP’s structured engagement model and its deliberate focus on SMEs as drivers of inclusive industrial growth.
He reaffirmed the readiness of the organised private sector to collaborate closely with NCSP in mobilising enterprises, providing structured policy feedback, and ensuring measurable enterprise-level outcomes from Nigeria–China economic engagements.
Both sides identified practical pathways to integrate SMEs into manufacturing value chains linked to Chinese partnerships; expand agro-processing and value-added production; strengthen technical and vocational education collaborations to close industrial skills gaps; and promote the development of geo-cluster industrial parks capable of anchoring regional manufacturing ecosystems.
They agreed to establish a formal working interface to translate strategic alignment into measurable results, with defined focus areas including investment facilitation, SME capacity development, industrial cluster formation, and export-oriented growth.
The meeting underscores NCSP’s resolve to convert diplomatic goodwill into tangible economic gains, expand opportunities for Nigerian businesses and strengthen productive capacity, leveraging NACCIMA’s network, the statement added, saying this aligns with President Bola Tinubu’s Renewed Hope Agenda, which seeks to achieve sustained and inclusive growth anchored on industrial productivity and private-sector dynamism.
Economy
Nigeria’s Inflation Eases Further to 15.1% in January 2026

By Adedapo Adesanya
Nigeria’s headline inflation rate eased further to 15.10 per cent in January 2026, down from 15.15 per cent in December 2025, continuing the moderation that started in the latter months of 2025.
According to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), Consumer Price Index (CPI) declined to 127.4 points in January 2026, reflecting a 3.8-point decrease from the preceding month of December 2025, which came in as 131.2 points.
The data, which is the first of the year, beat analysts’ expectations, which had expected an 18 per cent growth. Instead, the January 2026 print showed a decrease of 0.05 per cent compared to the December 2025 Headline inflation rate.
On a year-on-year basis, the inflation rate was 12.51 per cent lower than the rate recorded in January 2025 (27.61 per cent). This shows that the Headline inflation rate (year-on-year basis) decreased in January 2026 compared to the same month in the preceding year.
On a month-on-month basis, the Headline inflation rate in January 2026 was -2.88 per cent, which was 3.42 per cent lower than the rate recorded in December 2025 (0.54 per cent). This means that in the review month, the rate of increase in the average price level was lower than the rate of increase in the average price level in December last year.
The percentage change in the average CPI for the twelve months ending January 2026 over the average for the previous twelve-month period was 21.97 per cent, showing a 4.37 per cent increase compared to 17.59 per cent recorded in January 2025.
Nigeria’s food inflation rate in January 2026 was 8.89 per cent on a year-on-year basis. This was 20.73 percentage points lower compared to the rate recorded in January 2025 (29.63 per cent).
On a month-on-month basis, the Food inflation rate in January 2026 was -6.02 per cent, down by 5.66 per cent compared to December 2025 (-0.36 per cent).
The decline can be attributed to the rate of decrease in the average prices of water yams, eggs, green peas, groundnut oil, soya beans, palm oil, maize (corn) grains, guinea corn, beans, beef meat, melon (egusi) unshelled, cassava tuber, and cow peas (white).
The NBS data showed that the average annual rate of food inflation for the twelve months ending January 2026 over the previous twelve-month average was 20.29 per cent, which was 18.18 percentage points lower compared with the average annual rate of change recorded in January 2025 (38.47 per cent).
Economy
Terrahaptix Secures Additional $22m from Investors, Valuation Hits $100m

By Adedapo Adesanya
Nigerian defence technology startup, Terra Industries, has extended its funding round to $34 million after securing an additional $22 million from investors, making it a $100 million company.
The new capital round was led by venture firm Lux Capital, with injections from the chief executive officer of Lagos-based unicorn Flutterwave, Mr Gbenga Agboola, as well as angel investors such as American actor Jared Leto and Jordan Nel.
The company said in a statement on Monday that the round was completed in under two weeks.
This comes weeks after it raised $11.75 million in January. That funding round was led by 8VC founded by the co-founder of Palantir Technologies Inc., Mr Joe Lonsdale. Other investors included Valor Equity Partners, Lux Capital, SV Angel, Leblon Capital GmbH, Silent Ventures LLC, Nova Global and angel investors, including Mr Meyer Malka — the managing partner of Ribbit Capital.
Some of the investors in the new round included 8VC, Nova Global, Silent Ventures, Belief Capital, Tofino Capital, and Resilience17 Capital, founded by Flutterwave CEO.
Terrahaptix, founded by Mr Nathan Nwachukwu and Mr Maxwell Maduka, will use the new funding to expand Terra’s manufacturing capacity as it expands into cross-border security and counter-terrorism.
The extension also comes amid growing international expansion. Earlier this month, Terra announced a partnership with Saudi industrial giant AIC Steel to launch a manufacturing hub in Saudi Arabia focused on producing infrastructure security systems.
In the coming weeks, the company also plans to unveil a mega factory, an indication of the company’s growth and importance, particularly as the need for security has risen in recent years, as groups such as Islamic State and al-Qaeda are gaining ground in Africa, converging along a swathe of territory that stretches from Mali to Nigeria.
According to Mr Nwachuku, the initial $11.75 million raise created significant momentum for the company, enabling it to close the additional $22 million in just under two weeks.
He added that beyond capital, the investors were selected for their experience building similar hard-tech and defence-focused companies.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn













