Economy
Nigeria: Moody’s Predicts 2.5% GDP Growth in 2017, 4% in 2018
**Affirms Country’s B1 Rating With Stable Outlook
By Modupe Gbadeyanka
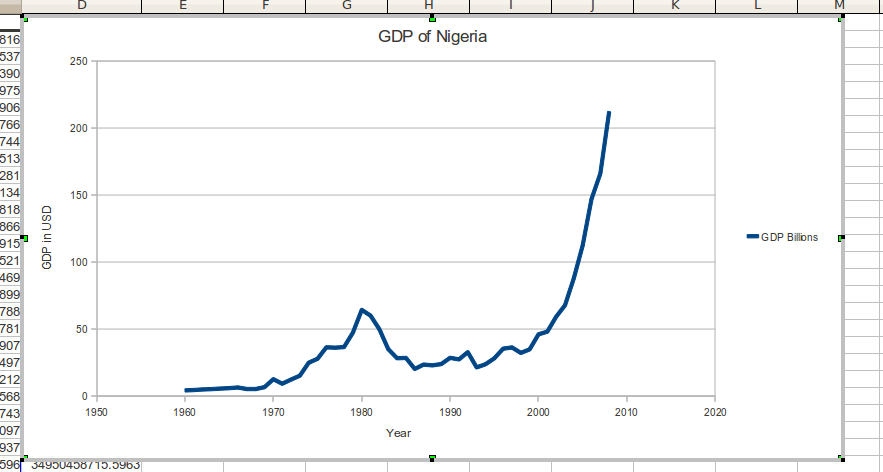
Moody’s Investors Service on Friday affirmed the B1 long-term issuer rating of the government of Nigeria with a stable outlook just as it forecasts that real GDP growth will rise to 2.5 percent in 2017 and accelerate further in 2018 to 4 percent.
The global rating firm disclosed that the key drivers for these were the medium term growth prospects remain robust despite the current challenging environment, with the rebound in oil production helping to rebalance the economy over the next two years; and the government’s balance sheet, which it said remains strong relative to its peers, resilient to the contractionary environment and temporarily elevated interest payments while the authorities pursue their efforts to grow non-oil taxes.
The long-term local-currency bond and deposit ceilings remain unchanged at Ba1. The long-term foreign-currency bond and deposit ceilings remain unchanged at Ba3 and B2, respectively.
Moody’s said it expects Nigeria’s medium term growth to remain robust, driven by the recovery in oil output and also over the near term, it expects Nigeria’s economic growth and US dollar earnings to improve in 2017, supported by a recovery in oil production.
According to Moody’s, after an estimated -1.5 percent real GDP growth in 2016, it forecasts real GDP growth to rise to 2.5% in 2017 and accelerate further in 2018 to 4%. A rebound in oil production to two million barrels per day (mbpd) will, if sustained, enhance economic growth and support the US dollar supply in the economy.
It noted that Nigeria has made significant gains in terms of governance and transparency in the oil sector. Improved availability of data, progress in restructuring the Nigerian National Petroleum Company (NNPC), rising effectiveness of operations at the refineries and a readiness to tackle difficult issues with partners (such as funding issues at the Joint Ventures) speak to a material improvement in the operating environment. The Petroleum Investment Bill (PIB bill), which had been blocked for 8 years in parliament, has been reactivated with a portion of the law drafted and passed by the Senate. Moreover, militant activity in the Niger Delta is set to wane following the resumption of payments from the government, though it will remain a threat to the recovery of the economy.
Moody’s further said the economy is also likely to benefit from the more timely implementation of the 2017 budget than its predecessor and in particular from the increase in capital spending on infrastructure which that will allow.
It also said the scarcity of Dollars, worsened by the soft capital controls imposed by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), is likely to continue to negatively affect important sectors of the economy especially in services and manufacturing sectors.
“We do not expect the current policy mix to significantly change over the short term but a gradual easing of restrictions is possible as foreign currency receipts improve with rising oil production,” the firm said on Friday in a statement obtained by Business Post.
In 2017 and 2018, we expect Nigeria’s balance of payments to move back into surplus, supported by government external borrowings and a falling current account deficit. The latter is quickly reducing, supported by falling imports and increased oil production.
Depreciation of the naira, soft capital controls and current dollar scarcity have been relatively effective at constraining imports. We expect foreign exchange reserves to grow modestly in 2017. While improved foreign investor sentiment should support the rebalancing of the economy over the medium term, with the return of portfolio investors improving dollar liquidity in the country, the continued existence of a parallel, unofficial foreign exchange market is likely to act as a strong deterrent over the near term.
RESILIENT GOVERNMENT BALANCE SHEET STRONGER THAN PEERS’ DESPITE TURBULENCE
Moody’s says it expects the medium-term impact of the oil price shock on Nigeria’s government balance sheet to be contained, and recent erosion of debt affordability to be reversed.
The effect of the recent downturn on the government’s budget sheet has been contained as the authorities have been able to offset the shortfall in revenue with large cuts in capital expenditure. As a result, Moody’s forecasts a budget deficit of 3 percent of GDP in 2016, comprised of a 2 percent of GDP federal government budget deficit and around 1% of arrears split between federal, state and municipality levels of government, it explained.
Moody’s forecasts the federal government deficit to remain around 2% of GDP in 2017 and 2018, with large capital expenditure outlays resuming as the government’s cash flow situation improves. Based on these underlying projections, Nigeria’s balance sheet will continue to compare favourably with peers’, with government debt remaining well below 20% of GDP over the coming years against 55% median for B1-rated peers.
By end-2016, Moody’s estimates the government debt stock will be comprised of 85% domestic borrowing and 15% external debt, resulting in a manageable external debt profile. Government external debt amounts to just 2.9% of GDP, with interest payments set to remain low, at around $330 million dollars per annum. Domestic debt has increased significantly in recent years, reaching its current level of NGN10 trillion. Around 30% of this debt is comprised of costly T-bills, which have increased refinancing risk and interest rate exposure. However, Moody’s expects the ratio of interest payments to government revenues to peak at 20% for general government, and close to 40% of revenues for federal government in 2017.
Although debt service costs are high, Nigeria’s domestic capital market is sufficiently developed to accommodate the yearly public sector borrowing requirements of around NGN5.5 trillion. This is another positive credit feature that distinguishes Nigeria from many similarly rated peers. The country’s banking sector is well-capitalised and liquid and the national pension fund still has additional capacity. Should banking sector liquidity decline, the Central Bank of Nigeria has tools at its disposal to support appetite for government securities, including lowering the cash reserve requirement ratio from its presently high level of 22.5%. However, appetite for government securities remains strong, with all instruments remain oversubscribed.
Moody’s expects the recent increase in debt service costs to prove temporary, as a result of i) the government’ initiatives to expand the non-oil revenue base, and ii) efforts to improve the structure of government debt.
Measures by the Federal Revenue Inland Service are expected to increase non-oil revenue to around NGN4 trillion in 2016 from NGN2.5 trillion in 2015. These include a tax amnesty on penalties and interest on tax liabilities due in 2013, 2014 and 2015. However, not all the initiatives have proven successful: the independent re-appropriation of revenues from the ministries departments and agencies (MDAs) has yielded disappointing results so far. Such outcomes highlight the considerable execution risks inherent in the transition to a less oil-dependent federal budget, and the implications for the government balance sheet should it not meet its objectives.
The government’s medium-term debt strategy should also help to lower the interest burden. The debt strategy is geared towards exchanging costly short-term debt with long-term concessional borrowing. Although a portion of future external borrowings are expected to be raised through the Eurobond markets, this is likely to be complemented with ongoing support from other multilateral institutions including the African Development Bank and the World Bank. The combined effect of these measures should help to bring interest payments/general government revenues down to 16.8% by 2018, from an estimated 19.8% in 2016.
RATIONALE FOR THE OUTLOOK AT STABLE
The stable outlook is driven by Moody’s view that the downside risks posed by the weakening of the country’s fiscal strength, and the external and economic pressures anticipated this year and next, are balanced by Nigeria’s strengths, which exceed those of sovereigns rated below B1. In 2016, Nigeria’s external vulnerability indicator of 31% will remain far below the expected B1 median of 51%, while its debt-to-GDP of 16.6% will remain far below the expected B1 median of 55%. Set against that, its expected debt servicing burden in terms of interest payments to revenue of 19% is more than double the B1 median of 9%. To a large extent, Moody’s believes that this reflects Nigeria’s underdeveloped public sector revenue base, a credit weakness that the administration is attempting to address.
WHAT COULD CHANGE THE RATING UP
Positive pressure on Nigeria’s issuer rating will be exerted upon: 1) successful implementation of structural reforms by the Buhari administration, in particular with respect to public resource management and the broadening of the revenue base; 2) strong improvement in institutional strength with respect to corruption, government effectiveness, and the rule of law; 3) the rebuilding of large financial buffers sufficient to shelter the economy against a prolonged period of oil price and production volatility.
WHAT COULD CHANGE THE RATING DOWN
Nigeria’s B1 issuer rating could be downgraded in the event of 1) a greater-than-anticipated deterioration in the government’s balance sheet or continued erosion of debt affordability, for example resulting from the failure to implement revenue reform; and 2) lower than expected medium term growth, for example as a result of delays in implementing key structural reforms, especially in the oil sector, or continued militancy in the Niger Delta, which undermine the level of oil production over the medium-term.
GDP per capita (PPP basis, US$): 6,184 (2015 Actual) (also known as Per Capita Income)
Real GDP growth (% change): -1.5% (2016 Estimate) (also known as GDP Growth)
Inflation Rate (CPI, % change Dec/Dec): 19% (2016 Estimate)
Gen. Gov. Financial Balance/GDP: -2.9% (2016 Estimate) (also known as Fiscal Balance)
Current Account Balance/GDP: -0.6% (2016 Estimate) (also known as External Balance)
External debt/GDP: 4.2% (2016 Estimate)
Level of economic development: Low level of economic resilience
Default history: No default events (on bonds or loans) have been recorded since 1983.
On 7 December 2016, a rating committee was called to discuss the ratings of the Government of Nigeria. The main points raised during the discussion were: The issuer’s economic fundamentals, including its economic strength, have not materially changed. The issuer’s fiscal or financial strength, including its debt profile, has not materially changed. The issuer’s susceptibility to event risks has not materially changed. Other views raised included: the issuer’s institutional strength/framework, have not materially changed. The issuer’s governance and/or management, have not materially changed.
The principal methodology used in these ratings was Sovereign Bond Ratings published in December 2015. Please see the Rating Methodologies page on www.moodys.com for a copy of this methodology.
The weighting of all rating factors is described in the methodology used in this credit rating action, if applicable.
Economy
Beta Glass Rejigs Board to Drive Next Phase of Innovation, Growth

By Aduragbemi Omiyale
The board of Beta Glass Plc has been reorganised, with the addition of four new executives, who will help to drive the company’s next phase of innovation and growth.
In a statement, Beta Glass announced the appointments of four non-executive directors, who are Mr Nitin Kaul, Ms Olusola Carrena, Mr Bolaji Olatunbosun Osunsanya, and Mr Boye Olusanya.
They are replacing the departing Mr Emmanouil Metaxakis, Mr Vassilis Kararizos, Mr Serge Joris, and Mr Gagik Apkarian from the board.
Their appointments, however, are subject to the ratification of the shareholders of the organisation at the next Annual General Meeting (AGM) on June 26, 2026.
Mr Kaul brings to the team over 25 years of global experience in strategy, mergers and acquisitions, restructuring, and business transformation across developed and emerging markets. He is a Partner, Portfolio Operations and member of the Executive Committee at Helios Investment Partners. Prior to joining Helios, he co-founded a boutique advisory firm focused on M&A and operational improvement for private businesses. He previously served as President of diversified industrial and aftermarket businesses at Gates Corporation, where he
was part of the executive team that led its sale to Blackstone in 2014. Earlier in his career, he held senior leadership roles at Tomkins and began his professional journey at Arthur Andersen. He currently serves on the boards of several companies across emerging markets.
As for Ms Carrena, she is a highly respected financial services leader with over 23 years of experience across investment banking, private equity, and corporate finance in Africa. She serves as Managing Director (Nigeria) on the Investment Team at Helios Investment Partners, where she oversees deal origination, execution, exits, and portfolio management across sectors. Before this, she spent a decade at Stanbic IBTC Capital Limited, rising to Executive Director and Head of Corporate Finance. During her tenure, she led and closed over 30 transactions valued at more than $4 billion across diverse industries, including oil and gas, FMCG, financial services, infrastructure, and healthcare. A CFA Charterholder, she holds a Master’s degree from the University of Alberta and a First-Class degree from the University of Lagos.
For Mr Osunsanya, he is an accomplished CEO, investor, and governance leader with more than 35 years of experience spanning energy, finance, and infrastructure. He previously served as Group CEO of Axxela Ltd., where he led strategic restructuring and significant value growth initiatives. Earlier, he held executive leadership roles at Oando PLC and Access Bank Plc, contributing to business transformation, governance strengthening, and sustainable expansion. He has served on the boards of several publicly listed and private companies, providing oversight in areas of strategy, audit, risk, and corporate governance, and remains an influential voice in Nigeria’s energy and financial sectors.
On the part of Mr Olusanya, he is a transformative business leader with over three decades of cross-industry experience spanning engineering, telecommunications, manufacturing, and agribusiness. He currently serves as chief executive of Flour Mills of Nigeria Plc, where he is leading a strategic transformation agenda focused on value chain integration, sustainability, and digital innovation. He previously served as Chief Executive Officer of 9mobile and as Chief Transformation Officer at Dangote Industries Limited, driving enterprise-wide restructuring and operational efficiency programs. He also served as Group Operating Partner at Helios Investment Partners, overseeing performance optimisation across portfolio companies. In addition, he is Vice Chairman of the Nigerian Economic Summit Group, contributing to national economic policy dialogue and private-sector development.
Economy
Dangote Refinery Cuts Ex-Depot Prices of Petrol, Diesel as Oil Tumbles

By Adedapo Adesanya
Dangote Petroleum Refinery has reduced its ex-depot prices for Premium Motor Spirit (PMS) and Automotive Gas Oil (AGO), marking the first downward adjustment after several sharp increases recorded in recent days.
According to the refinery’s latest pricing template released on March 10, 2026, the gantry price of petrol has been cut by N100 to N1,075 per litre, down from N1,175 per litre previously.
The 650,000 barrels per day capacity refinery also disclosed that PMS supplied through coastal distribution will now sell at N1,050 per litre, reflecting a marginal price differential for marine deliveries.
In addition, the gantry price of AGO, commonly known as diesel, has been reduced to N1,430 per litre, representing a N190 drop from the earlier price of N1,620 per litre.
The company noted that the quoted gantry prices exclude statutory charges imposed by the Nigerian Midstream and Downstream Petroleum Regulatory Authority (NMDPRA).
The price adjustment came amid a recent decline in global crude oil prices, which has started to ease cost pressures across the international petroleum market and is influencing pricing trends in the downstream sector.
US President Donald Trump reassured markets and claimed the war would end soon, but Iran on Tuesday vowed not to let “a litre” of oil be exported from the Middle East until the United States and Israel stop bombing it.
Brent crude price, which hit a high of $109 per barrel, has now dropped to $90 per barrel, as the largest oil producers in the Middle East Gulf have deepened production cuts and are already lowering output by a combined more than 5 million barrels per day, as the blockade of the Strait of Hormuz has started to affect upstream production.
However, there are worries that, unlike the speed at which petrol stations hiked their cost at the pump, the revised ex-depot prices will not reflect through depot channels and translate into lower retail pump prices nationwide.
Economy
Petrol Station Owners Urge NNPC to Expand Local Refining to Withstand Global Oil Shocks

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Petroleum Products Retail Outlets Owners Association of Nigeria (PETROAN) has urged the Nigerian National Petroleum Company (NNPC) Limited to urgently strengthen domestic refining capacity to shield the country from global petroleum market shocks.
The National President, PETROAN, Billy Gillis-Harry, on Monday called on the Group Chief Executive Officer of the state oil company, Mr Bayo Ojulari, to facilitate the immediate commencement of production at Nigeria’s local refineries.
Mr Gillis-Harry said that production at the refineries was paramount, particularly the Area five Plant at Port Harcourt Refinery and the Warri Refinery, which previously operated briefly before shutdown for profit index evaluation.
He said that this had become imperative due to the ongoing conflict involving Israel, the United States and Iran, which was pushing global petroleum prices to alarming levels.
Projecting future trends, he warned that Premium Motor Spirit (PMS) could rise close to N2,000 per litre while Automotive Gas Oil (AGO) may approach N3,000 per litre if the situation persists.
He said that sustained drone and missile attacks now threaten critical oil routes and infrastructure, creating uncertainty in global supply chains.
“With no clear end to the conflict, petroleum product prices in both international and domestic markets are expected to rise sharply in the coming days.
“Before the crisis, PMS, known as fuel sold at N774 per litre, but now sells above N1,000 per litre, representing an increase of about 30 per cent.
“Diesel, previously sold at N950 per litre, has risen to N1,400 per litre and above, an increase of about 49 per cent,” he said.
Mr Gillis-Harry said that rehabilitating Nigeria’s refineries for immediate domestic production was critical.
On local refining, he said that it would reduce exposure to international market volatility, especially as Nigeria had abundant crude oil resources under the custody of NNPC Limited.
He said that government-owned refineries were less vulnerable to global supply disruptions compared to privately owned refineries dependent on imported crude.
The PETROAN president said that continued fuel price increases would worsen inflation, cause job losses, deepen economic hardship, increase transportation costs, and raise prices of goods and services nationwide.
“Fuel remains essential for daily mobility, while diesel is vital for manufacturing and industrial operations,” he said.
He commended President Bola Tinubu for the ongoing bold policies to reform the oil and gas sector, and called on Tinubu to direct the immediate rehabilitation and commencement of production at the government-owned refineries.
According to him, this will ultimately bring relief to citizens and stimulate economic growth.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn




















