World
Funding Africa’s Infrastructure Gap
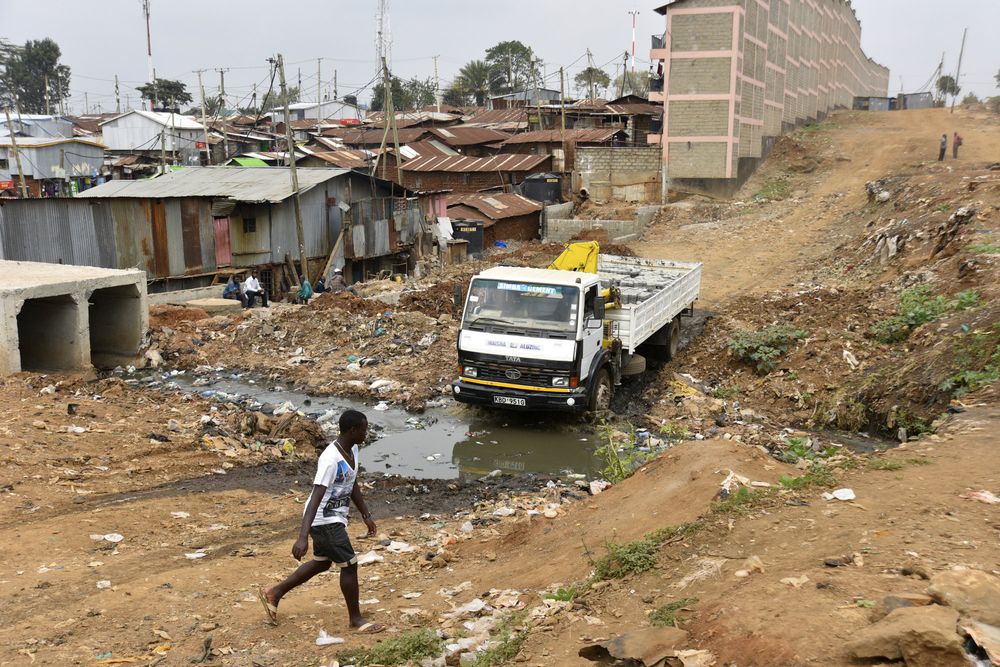

Key to enabling African economies to make the most of their opportunities is developing infrastructure in the region. Across the continent, new laws are being implemented and alternative sources of infrastructure funding are being sought in order to kick-start direly needed infrastructure projects. At the centre of it all is China, which is providing alternative sources financing to countries in Africa that have not been able to access funding in more traditional ways. The benefits are numerous, but African countries are also concerned about their growing dependence on China.
Research released in 2018 from Baker McKenzie and IJGlobal (research) with data drawn exclusively from fully financed projects and excluding recent announcements of government funding commitments, shows that the value of loans from Chinese financing of energy and infrastructure projects in Africa almost trebled between 2016 and 2017, from $3 billion to $8.8 billion..
“As China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), a multi-billion dollar plan to link Asia, Europe and Africa, is actively being implemented, we expect this amount will increase even further in the coming years,” says Wildu du Plessis, Head of Banking & Finance at Baker McKenzie in Johannesburg.
According to the research, Chinese banks have been active lenders to infrastructure projects in 19 different countries in Africa in the past four years. Infrastructure projects in Ethiopia have received $1,8 billion since 2014, Kenyan projects $4,8 billion, Mozambique infra deals $1,6 billion and Nigerian projects $5 billion from Chinese lenders. South African infrastructure projects have received $2.2 billion from Chinese lenders since 2014, Zambia has received $1.5 billion and Zimbabwe has seen $1.3 billion in loans from Chinese policy lenders since 2014.
As one of South Africa’s largest trading partners, China plays an important role in infrastructure investment in this country too. At the BRICS Summit Energy in 2018, China pledged to invest USD 14.7bn in South Africa and to grant loans to state owned enterprises Eskom and Transnet.
Du Plessis notes that even though the South African infrastructure funding gap is not as severe as other countries in Africa, there is a still difficulty in mobilising funds for infrastructure development and related projects because traditional funders take time to decide on whether to get involved.
Stanley Jia, Partner in the Beijing Office of Baker McKenzie, notes, “As part of the mobilisation of different sources of funding to fill the infrastructure gap, there is a big bucket of Chinese funding that can be used for infrastructure projects in Africa. The increasing appetite from China for funding infrastructure projects as part of its BRI means they are happy to partner with local development finance institutions and other international funders.”
According to Kieran Whyte, Head of Energy, Mining & Infrastructure at Baker McKenzie in Johannesburg, “A big attraction of the BRI for both African governments and project sponsors is that it assists the speed of project implementation. Project stakeholders advise that the whole process is a lot quicker than other options.”
Jia notes that, “Chinese policy lenders also assist in providing liquidity in that they are willing to negotiate with countries that have financial constraints that deny them access to traditional capital.”
Du Plessis notes, however, that there is rising concern amongst African sovereigns who are worried about the long term effects on their dependence on China.
“This is even though China has reiterated that it wants to be considered a responsible investor in Africa. It remains to be seen whether this concern has an impact on Chinse involvement in the funding infrastructure projects in future years. African countries have also begun building capacity to correct the imbalance between borrowers and lenders in the negotiation phase so that more balanced agreements can be reached,” he explains.
Senegal and Côte d’Ivoire
Khaled Abou El Houda, Managing Partner of Houda Law Firm in Senegal and Côte d’Ivoire, notes, “Senegal became a BRI partner with China after the two countries signed bilateral deals during Chinese President Xi Jinping’s West Africa trip in late July 2018.
“In addition to plans for improving infrastructure in Senegal, China promised to support the country with anti-terror, peacekeeping and maintaining social stability. However, while the BRI has provided many opportunities for development, the general consensus is the China-Africa relationship could be placed on more equal footing. The challenge for Africa is in establishing where its interests converge with China’s, where they diverge, and how areas of convergence can be shaped to advance African development priorities,” he says.
Houda explains that in order to help fund the infrastructure gap, the Senegalese government adopted the Plan Senegal Emergent (PSE) in 2014, with the overall aim of boosting the economy.
“We saw encouraging signs of 6.8% real GDP growth one year after the PSE’s implementation and it has maintained more than 6% growth in subsequent years. Building on this success, the government is continuing its PSE implementation and related reforms, targeting sectors such as energy, transport infrastructure and agriculture.”
Zimbabwe
In Zimbabwe, Thomas Chagudumba, of Atherstone & Cook notes that the infrastructure funding gap is being addressed in various ways. Funding comes through government floating infrastructure bonds, Public Private Partnerships (PPPs) and off-budget loan funding. Khumalo notes that policy consistency, particularly in respect of currency convertibility, exchange control regulations on repatriation of funds and improved transparency and accountability are all essential to encourage infrastructure funding in Zimbabwe. Further, he explains that it is important to ring fence resources, including foreign currency, for critical inputs in support of ongoing works. This can be done via undertakings from the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe and government guarantees. Construction and performance bonds could also be used to curb poor project implementation, mismanagement and corruption in the infrastructure sector.
Chagudumba notes that Zimbabwe has also benefited from the BRI with major projects in Zimbabwe including the Kariba South Hydro Power Station and the Victoria Falls International Airport.
“For Zimbabwe, the benefits of the BRI include that it aids in infrastructure development, which in turn benefits economic expansion. The transfer of information and expertise and employment creation are further benefits.”
Mauritius
Mauritius does not have a large infrastructure funding gap as compared to other jurisdictions in Africa, explains Moorari Gujadhur, a barrister at Madun Gujadhur Chambers in Mauritius. “Infrastructure projects in Mauritius tend to focus on either improving current infrastructure (ie large grid separated flyovers) or to introduce new projects (ie light rail transport). These tend to be government to government,” he says.
He explains, “India has provided Mauritius with a grant and loan to fund the development of a light rail transport project, whilst China is making investments in the ports. The new Mauritian airport terminal was entirely funded by China.”
Ethiopia
In Ethiopia meanwhile, bridging the infrastructure gap is more complicated. Mehrteab Leul, Principal of Mehrteab Leul & Associates Law Office in Ethiopia, explains, “In February this year, Ethiopia enacted a new proclamation facilitating PPPs called the Public-Private Partnership Proclamation. According to the proclamation, it is within the powers of the PPP Board to approve PPP projects as well as instruct public bodies/enterprises to carry out a certain project as a PPP.
“According to the policy document, one of the main objectives for PPP projects is to increase the financial resources available for the development of infrastructure services in Ethiopia. All of the 17 recently approved under the PSE centre around the delivery of infrastructure services,” he notes.
Leul says that China and Italy are the prime role players infrastructure investment in Ethiopia. They have made a significant impact on the sector including via developing electricity generation capacity, supplying drinking water in urban and rural areas, developing road infrastructure and building hospitals and other infrastructure investments.
“Since 1957 the Italian contractor Salini Impregilo has completed 20 major projects in Ethiopia, worth a total of €9 billion. Chinese infrastructure investment in Ethiopia totalled $4.7 billion between 2009 and 2012.”
Leul says that in terms of the BRI, a strong win- in situation has developed for both China and Ethiopia.
“In particular, the country has benefited from infrastructure development funding, as well as technological transformation from China to Ethiopia and job creation. In general, it will enable both countries to optimize the benefits from the global market. The Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway project is a working example of benefits of the BRI,” he says.
Leul cautioned however, that the BRI, “might leave the country open to the risk of troubled debt pressure and increasing dependence on China.”
Tunisia
Omar Besbes of United Advisers in Tunisia notes that all North African countries have signed the Belt and Road Initiative with China. However, the benefits received from this initiative are divergent. While in Tunisia it is only focused on studies of infrastructure projects so far, in Algeria and Morocco some infrastructure projects are already implemented such as seaports and desalination plants.
For North African in countries, the benefits of the BRI are that it allows recipient countries to not have to depend on traditional donors, and gives them the opportunity to benefit from China’s growth. Besbes says that countries other than China that have played a substantial role in infrastructure investment in North Africa include the European Union, Japan France and Germany. As a result on their funding, roads, bridges, ports, airports, electricity production stations and desalination plants have been built in the region.
World
Iranian Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei Dies After Air Strikes

By Dipo Olowookere
Iranian Supreme Leader, Mr Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, has died after coordinated airstrikes carried out by the United States and Israel on Tehran on Saturday morning.
His death was confirmed on Sunday morning by Iranian state media, which also disclosed that his daughter and grandchild were among those killed in the bombardment, which destroyed his compound.
Mr Khamenei was killed during a meeting with top leaders of the Middle East country yesterday, including the Defence Minister Amir Nasirzadeh and Revolutionary Guard commander Mohammad Pakpour, who reportedly died too.
His elimination has sparked mixed reactions, with some Iranians on the streets celebrating his demise, and others condemning the joint air strikes.
The President of the United States, Mr Donald Trump, described the late Iranian leader as “one of the most evil people in history,” expressing satisfaction at the action, which he said was “successful,” as it represented justice for both Iranians and Americans.
Meanwhile, Tehran has vowed to further respond to the attacks after initially firing missiles at six neighbours, including Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE, Bahrain, and Jordan.
Flight operations in the region have been disrupted because of the retaliatory action of Iran over the weekend, though most of the missiles were intercepted.
World
AfBD, AU Renew Call for Visa-Free Travel to Boost African Economic Growth
By Adedapo Adesanya
The African Development Bank (AfDB) and the African Union have renewed their push for visa-free travel to accelerate Africa’s economic transformation.
The call was reinforced at a High-Level Symposium on Advancing a Visa-Free Africa for Economic Prosperity, where African policymakers, business leaders, and development institutions examined the need for visa-free travel across the continent.
The consensus described the free movement of people as essential to unlocking Africa’s economic transformation under the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA).
The symposium was co-convened by AfDB and the African Union Commission on the margins of the 39th African Union Summit of Heads of State and Government in Addis Ababa.
The participants framed mobility as the missing link in Africa’s integration agenda, arguing that while tariffs are falling under AfCFTA, restrictive visa regimes continue to limit trade in services, investment flows, tourism, and labour mobility.
On his part, Mr Alex Mubiru, Director General for Eastern Africa at the African Development Bank Group, said that visa-free travel, interoperable digital systems, and integrated markets are practical enablers of enterprise, innovation, and regional value chains to translate policy ambitions into economic activity.
“The evidence is clear. The economics support openness. The human story demands it,” he told participants, urging countries to move from incremental reforms to “transformative change.”
Ms Amma A. Twum-Amoah, Commissioner for Health, Humanitarian Affairs and Social Development at the African Union Commission, called for faster implementation of existing continental frameworks.
She described visa openness as a strategic lever for deepening regional markets and enhancing collective responses to economic and humanitarian crises.
Former AU Commission Chairperson, Ms Nkosazana Dlamini-Zuma, reiterated that free movement is central to the African Union’s long-term development blueprint, Agenda 2063.
“If we accept that we are Africans, then we must be able to move freely across our continent,” she said, urging member states to operationalise initiatives such as the African Passport and the Free Movement of Persons Protocol.
Ghana’s Trade and Industry Minister, Mrs Elizabeth Ofosu-Adjare, shared her country’s experience as an early adopter of open visa policies for African travellers, citing increased business travel, tourism, and investor interest as early dividends of greater openness.
The symposium also reviewed findings from the latest Africa Visa Openness Index, which shows that more than half of intra-African travel still requires visas before departure – seen by participants as a significant drag on intra-continental commerce.
Mr Mesfin Bekele, Chief Executive Officer of Ethiopian Airlines, called for full implementation of the Single African Air Transport Market (SAATM), saying aviation connectivity and visa liberalisation must advance together to enable seamless travel.
Regional representatives, including Mr Elias Magosi, Executive Secretary of the Southern Africa Development Community, emphasised the importance of building trust through border management and digital information-sharing systems.
Ms Gabby Otchere Darko, Executive Chairman of the Africa Prosperity Network, urged governments to support the “Make Africa Borderless Now” campaign, while tourism campaigner Ras Mubarak called for more ratifications of the AU Free Movement of Persons protocol.
Participants concluded that achieving a visa-free Africa will require aligning migration policies, digital identity systems, and border infrastructure, alongside sustained political commitment.
World
Nigeria Exploring Economic Potential in South America, Particularly Brazil

By Kestér Kenn Klomegâh
In this interview, Uche Uzoigwe, Secretary-General of NIDOA-Brazil, discusses the economic potential in South America, particularly Brazil, and investment incentives for Brazilian corporate partners for the Federal Republic of Nigeria (FRN). Follow the discussion here:
How would you assess the economic potential in the South American region, particularly Brazil, for the Federal Republic of Nigeria? What investment incentives does Nigeria have for potential corporate partners from Brazil?
As the Secretary of NIDOA Brazil, my response to the questions regarding the economic potentials in South America, particularly Brazil, and investment incentives for Brazilian corporate partners would be as follows:
Brazil, as the largest economy in South America, presents significant opportunities for the Federal Republic of Nigeria. The country’s diverse economy is characterised by key sectors such as agriculture, mining, energy, and technology. Here are some factors to consider:
- Natural Resources: Brazil is rich in natural resources like iron ore, soybeans, and biofuels, which can be beneficial to Nigeria in terms of trade and resource exchange.
- Growing Agricultural Sector: With a well-established agricultural sector, Brazil offers potential collaboration in agri-tech and food security initiatives, which align with Nigeria’s goals for agricultural development.
- Market Size: Brazil boasts a large consumer market with a growing middle class. This represents opportunities for Nigerian businesses looking to export goods and services to new markets.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Brazil has made significant investments in infrastructure, which could create opportunities for Nigerian firms in construction, engineering, and technology sectors.
- Cultural and Economic Ties: There are historical and cultural ties between Nigeria and Brazil, especially considering the African diaspora in Brazil. This can facilitate easier business partnerships and collaborations.
In terms of investment incentives for potential corporate partners from Brazil, Nigeria offers several attractive incentives for Brazilian corporate partners, including:
- Tax Incentives: Various tax holidays and concessions are available under the Nigerian government’s investment promotion laws, particularly in key sectors like agriculture, manufacturing, and technology.
- Repatriation of Profits: Brazil-based companies investing in Nigeria can repatriate profits without restrictions, thus enhancing their financial viability.
- Access to the African Market: Investment in Nigeria allows Brazilian companies to access the broader African market, benefiting from Nigeria’s membership in regional trade agreements such as ECOWAS.
- Free Trade Zones: Nigeria has established free trade zones that offer companies the chance to operate with reduced tariffs and fewer regulatory burdens.
- Support for Innovation: The Nigerian government encourages innovation and technology transfer, making it attractive for Brazilian firms in the tech sector to collaborate, particularly in fintech and agriculture technology.
- Collaborative Ventures: Opportunities exist for joint ventures with local firms, leveraging local knowledge and networks to navigate the business landscape effectively.
In conclusion, fostering a collaborative relationship between Nigeria and Brazil can unlock numerous economic opportunities, leading to mutual growth and development in various sectors. We welcome potential Brazilian investors to explore these opportunities and contribute to our shared economic goals.
In terms of this economic cooperation and trade, what would you say are the current practical achievements, with supporting strategies and systemic engagement from NIDOA?
As the Secretary of NIDOA Brazil, I would highlight the current practical achievements in economic cooperation and trade between Nigeria and Brazil, alongside the supporting strategies and systemic engagement from NIDOA.
Here are some key points:
Current Practical Achievements
- Increased Bilateral Trade: There has been a notable increase in bilateral trade volume between Nigeria and Brazil, particularly in sectors such as agriculture, textiles, and technology. Recent trade agreements and discussions have facilitated smoother trade relations.
- Joint Ventures and Partnerships: Successful joint ventures have been established between Brazilian and Nigerian companies, particularly in agriculture (e.g., collaboration in soybean production and agricultural technology) and energy (renewables, oil, and gas), demonstrating commitment to mutual development.
- Investment in Infrastructure Development: Brazilian construction firms have been involved in key infrastructure projects in Nigeria, contributing to building roads, bridges, and facilities that enhance connectivity and economic activity.
- Cultural and Educational Exchange Programs: Programs facilitating educational exchange and cultural cooperation have led to strengthened ties. Brazilian universities have partnered with Nigerian institutions to promote knowledge transfer in various fields, including science, technology, and arts.
Supporting Strategies
- Strategic Trade Dialogue: NIDOA has initiated regular dialogues between trade ministries of both nations to discuss trade barriers, potential markets, and cooperative opportunities, ensuring both countries are aligned in their economic goals.
- Investment Promotion Initiatives: Targeted initiatives have been established to promote Brazil as an investment destination for Nigerian businesses and vice versa. This includes showcasing success stories at international trade fairs and business forums.
- Capacity Building and Technical Assistance: NIDOA has offered capacity-building programs focused on enhancing Nigeria’s capabilities in agriculture and technology, leveraging Brazil’s expertise and sustainable practices.
- Policy Advocacy: Continuous advocacy for favourable trade policies has been a key focus for NIDOA, working to reduce tariffs and promote economic reforms that facilitate investment and trade flows.
Systemic Engagement
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Engaging the private sector through PPPs has been essential in mobilising resources for development projects. NIDOA has actively facilitated partnerships that leverage both public and private investments.
- Trade Missions and Business Delegations: Organised trade missions to Brazil for Nigerian businesses and vice versa, allowing for direct engagement with potential partners, fostering trust and opening new channels for trade.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: NIDOA implements a rigorous monitoring and evaluation framework to assess the impact of various initiatives and make necessary adjustments to strategies, ensuring effectiveness in achieving economic cooperation goals.
Through these practical achievements, supporting strategies, and systemic engagement, NIDOA continues to play a pivotal role in enhancing economic cooperation and trade between Nigeria and Brazil. By fostering collaboration and leveraging shared resources, we aim to create a sustainable and mutually beneficial economic environment that promotes growth for both nations.
Do you think the changing geopolitical situation poses a number of challenges to connecting businesses in the region with Nigeria, and how do you overcome them in the activities of NIDOA?
The changing geopolitical situation indeed poses several challenges for connecting businesses in the South American region, particularly Brazil, with Nigeria. These challenges include trade tensions, shifting alliances, currency fluctuations, and varying regulatory environments. Below, I will outline some of the specific challenges and how NIDOA works to overcome them:
Current Challenges
- No Direct Flights: This challenge is obviously explicit. Once direct flights between Brazil and Nigeria become active, and hopefully this year, a much better understanding and engagement will follow suit.
- Trade Restrictions and Tariffs: Increasing trade protectionism in various regions can lead to higher tariffs and trade barriers that hinder the movement of goods between Brazil and Nigeria.
- Currency Volatility: Fluctuations in the value of currencies can complicate trade agreements, pricing strategies, and overall financial planning for businesses operating in both Brazil and Nigeria.
- Different regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements in both countries can create challenges for businesses aiming to navigate these systems efficiently.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Changes in global supply chains due to geopolitical factors may disrupt established networks, impacting businesses relying on imports and exports between the two nations.
Overcoming Challenges through NIDOA.
NIDOA actively engages in discussions with both the Brazilian and Nigerian governments to advocate for favourable trade policies and agreements that reduce tariffs and improve trade conditions. This year in October, NIDOA BRAZIL holds its TRADE FAIR in São Paulo, Brazil.
What are the popular sentiments among the Nigerians in the South American diaspora? As the Secretary-General of the NIDOA, what are your suggestions relating to assimilation and integration, and of course, future perspectives for the Nigerian diaspora?
As the Secretary-General of NIDOA, I recognise the importance of understanding the sentiments among Nigerians in the South American diaspora, particularly in Brazil.
Many Nigerians in the diaspora take pride in their cultural roots, celebrating their heritage through festivals, music, dance, and culinary traditions. This cultural expression fosters a sense of community and belonging.
While many individuals embrace their new environments, they often face challenges related to cultural differences, language barriers, and social integration, which can lead to feelings of isolation.
Many express optimism about opportunities in education, business, and cultural exchange, viewing their presence in South America as a chance to expand their horizons and contribute to economic activities both locally and back in Nigeria.
Sentiments regarding acceptance vary; while some Nigerians experience warmth and hospitality, others encounter prejudice or discrimination, which can impact their overall experience in the host country. NIDOA BRAZIL has encouraged the formation of community organisations that promote networking, cultural exchange, and social events to foster a sense of belonging and support among Nigerians in the diaspora. There are currently two forums with over a thousand Nigerian members.
Cultural Education and Awareness Programs: NIDOA BRAZIL organises cultural education programs that showcase Nigerian heritage to local communities, promoting mutual understanding and appreciation that can facilitate smoother integration.
Language and Skills Training: NIDOA BRAZIL provides language courses and skills training programs to help Nigerians, especially students in tertiary institutions, adapt to their new environment, enhancing communication and employability within the host country.
Engaging in Entrepreneurship: NIDOA BRAZIL supports the entrepreneurial spirit among Nigerians in the diaspora by facilitating access to resources, mentorship, and networks that can help them start businesses and create economic opportunities.
Through its AMBASSADOR’S CUP COMPETITION, NIDOA Brazil has engaged students of tertiary institutions in Brazil to promote business projects and initiatives that can be implemented in Nigeria.
NIDOA BRAZIL also pushes for increased tourism to Brazil since Brazil is set to become a global tourism leader in 2026, with a projected 10 million international visitors, driven by a post-pandemic rebound, enhanced air connectivity, and targeted marketing strategies.
Brazil’s tourism sector is poised for a remarkable milestone in 2026, as the country expects to welcome over 10 million international visitors—surpassing the previous record of 9.3 million in 2025. This expected surge represents an ambitious leap, nearly doubling the country’s foreign-arrival numbers within just four years, a feat driven by a combination of pent-up global demand, strategic air connectivity improvements, and a highly targeted marketing campaign.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn












