Feature/OPED
Candidates from Djibouti, Kenya, Madagascar and Mauritius Contesting for AUC Chairperson’s Position

By Professor Maurice Okoli and Dr Ken Onyeali Ikpe
The African Union Chairperson is an important position within the African Union. The Chairperson serves as the head of the (AU) African Union elected by the assembly of heads of state and government. As the African Union stands at a crossroads and a critical juncture, effective leadership is essential for addressing the myriad challenges facing the African continent.
After several months of conscientious search for potential contestants to take over the African Union Commission chairperson’s position, which expires next February 2025, four (4) candidates have emerged representing Djibouti, Kenya, Madagascar and Mauritius.
With these candidates already confirmed following the deadline set for submission of applications and all the necessary supporting documents, four senior African politicians are engaged in an intensive campaign and strategic lobbying across Africa. The deadline for candidacies closed on August 6, at the African Union, which is headquartered in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
The African Union, a continental organization consisting of 55 African Member States, is scheduled to hold elections at its summit in February 2025 to choose a successor to Moussa Faki Mahamat, chairperson of the African Union Commission. The election is conducted by secret ballot, and the winner must secure a majority of two-thirds of the vote among eligible member states.
According to the stipulated guidelines, the chairperson of the African Union Commission (AUC) is the chief executive officer who exercises administrative, legal, and financial functions. It also includes pursuing a leadership role in delivering the continental vision of an integrated transformative economy, consistently working for a prosperous and peaceful Africa. The current geopolitical situation requires engaging in beneficial relations with external development partners for the continent.
Considered Africa’s economic engine since its establishment as OAU and later transformed into AU, the head of the AUC, which is an executive body, is elected on a rotational basis between the regions of the continent for every four years and the elected chairperson can be re-elected for two terms as incorporated in the constitution. Africa has five distinctive regions: northern, western, central, southern and eastern. Quite apart from regional origin, the candidates are required to have serious educational qualifications and, most importantly, experience to handle effectively the multiple tasks as the chairperson of the AUC. (See AU report: African Union Commission Elections 2025).
Contesting Candidates
From preliminary research and monitoring, the central, western, and southern regions of Africa have already served as chairpersons, this implies it is the turn of southern and eastern candidates of Africa. Concretely, it therefore includes Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Rwanda, Seychelles, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. These countries can now, by geographical definition, produce candidates for the position of chairperson. One of the basic key criteria is the candidate must be a former president, former prime minister, or former foreign minister to take up the job which mostly includes the undertaking of “measures aimed at promoting and popularizing the objectives of the Union” and the execution of “such other functions as may be determined by the Assembly or the Executive Council.”
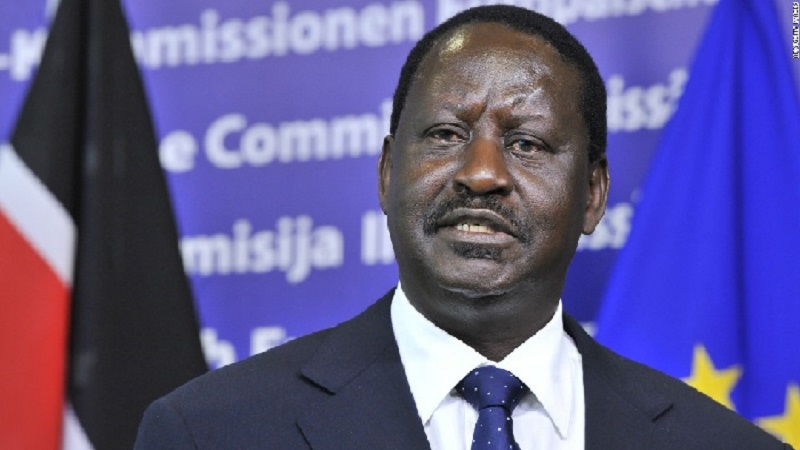
According to an African Union report, in early August 2024, the four confirmed candidates for this top AUC position, and to ultimately take over from the current chairperson Moussa Faki Mahamat, are Mahamoud Ali Youssouf of Djibouti, Raila Odinga of Kenya, Richard Randriamandrato of Madagascar and Anil Gayan of Mauritius.
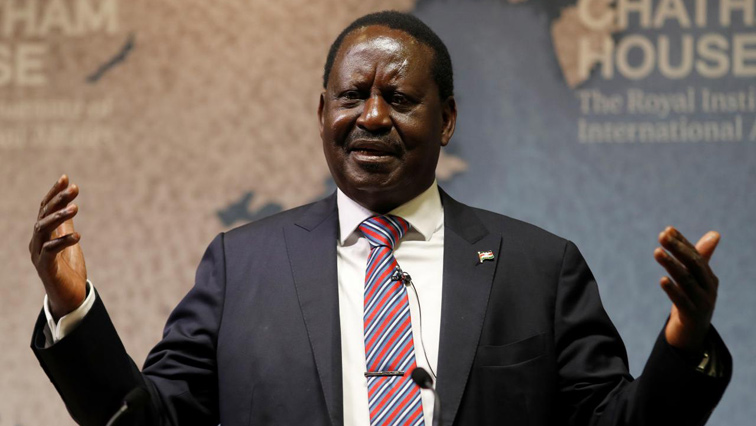
(i) Raila Odinga is a veteran Kenyan opposition leader, who now at 79, has tried and failed five times to become president, most recently losing the 2022 election to William Ruto. Odinga spent his years in politics, fighting for democracy during the autocratic rule of President Daniel Arap Moi. “We are focused on bringing the seat home for Kenya and serving the African people,” Odinga said on X while announcing his formal candidacy.
A media report released in March 2024, titled “Museveni Endorses Raila Odinga’s AU Chairperson Bid” and circulated in the East African region showed the publicity campaign and erratic steps at promoting Kenyan Raila Odinga to take over as Chairman of the AU Commission. Interestingly, Raila Odinga, Kenya’s opposition leader, has readily accepted Ugandan President Yoweri Museveni’s endorsement of his candidacy for African Union Commission chairperson.
In a flagship statement posted via his social media platforms, Odinga said Museveni endorsed him during a joint meeting with President William Ruto. The Azimio alliance’s leader stated that the joint meeting with President Museveni and President Ruto was organized at the Ugandan president’s invitation. Odinga has an unmistakable political influence. Born into a modest political family and grew up in politics. His profound perspectives suggest he operates as a pivotal figure within power dynamics and his decision-making capacity is perceived as absolute pragmatic. Odinga, most observers say, possesses an assertive leadership style and always expresses steadfast interest in the complexity of a development-oriented society. These leadership skills echo his deep-seated affection for a genuine communal, regional, and continental tradition. Odinga as a suitable candidate underscores the perfect choice to embrace and settle for the best administrator for Africa.
(ii) Richard Mahitsison Randriamandrato studied in Paris, France. Randriamandrato was Madagascar’s foreign minister from March to October 2022 but was fired after voting at the United Nations to condemn Russia’s annexations of four Ukrainian regions. Madagascar has followed a non-aligned position on the war in Ukraine. He is a prominent Malagasy politician known for his role in the government of Madagascar.
He served also as a minister of economy and finance from 2019 until 2021 where he focused on economic policies aimed at stabilizing and developing Madagascar’s economy. Beyond his ministerial roles, he has been involved in strategic foresight and economic intelligence advising on regional infrastructure and development projects.
(iii) Anil Gayan, 76, served as foreign minister of the Indian Ocean island nation of Mauritius between 1983 and 1986, and again from 2000 to 2003. After this, he has since held other posts including at the tourism and health ministries. His biography says Anil Gayan’s ancestors migrated from India when the island was a British colony. He studied law at the London School of Economics and the University of London until 1974. As a politician, he formed a political group called FNM (Front National Mauricien) in 2009. Along the line, in 2008, he was part of United Nations mediation in Guinea-Bissau. Gayan also led a 20-member African Union group of observers during the 2010 Rwanda elections.
(iv) Mahamoud Ali Youssouf, in April 2024, was nominated by Djibouti for the position of chairperson. His biography says that between 1985 and 1990, he studied foreign languages at the Lumière University Lyon and then studied business management at the University of Liverpool in the United Kingdom. He was, however, unsuccessful with his thesis at the Université libre de Bruxelles, Belgium.
Nevertheless, as a staunch politician, Youssouf believes that although Djibouti is a small country with a sizable port, his government hopes to develop its economy along the same lines as Dubai. Its strategic location serves as a conduit to the whole world. “I am the only candidate capable of bridging the gap between the different regions of Africa, being French-speaking, but also English-speaking and Arabic-speaking,” said Djibouti’s Youssouf, the 58-year-old has been the foreign minister of the tiny but strategic Horn of Africa nation since 2005. “My primary objective if I am elected is to silence the guns” on the continent, he told AFP in an interview in July.
Employment Implications
Bridging the gap between different regions implies that this AUC leadership will address the development dynamics in the continent. That further emphasizes creating a conducive environment and atmosphere for potential external investors and stakeholders within the geopolitical parameters, a mixed economy, speeding up the most industrialization processes, and working towards technological advancement in Africa. (See African Leaders Extraordinary Summit report, Feb. 2024)
Noticeably the republics of Burkina Faso, Chad, Niger and Mali have established governments, accused their previous political leaders of manipulation by external powers, economic under-developments and the deepening instability (that is un-quantify-able failure to stem the Islamist insurgency) in the Sahel-Saharan region, an elongated landlocked territory located between North Africa (Maghreb) and West Africa, to the Atlantic coast of West Africa.
During a series of summits, conferences and meetings that proliferated these years, the AUC reiterated the continuing growth of multiple democratic challenges with a wider negative impact across the continent and particularly itemized military takeovers that have become a distinctive feature (or accepted norm) of regime change in West Africa. Some experts pointed to the rising neo-colonial tendencies perpetrated by the former colonies and their indiscriminate scramble for resources on the continent. In addition, there are also overarching narratives of growing crisis and explicit signs of weaknesses on the side of regional economic blocs in the continent, to say the least, and appropriately under the direct confines of the African Union.
Researchers have reminded the African Union and the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) to invoke the African Convention for the Elimination of Mercenary, which went into effect in 1985, prohibiting states from allowing mercenaries into their territories. The researcher further called for addressing promptly ‘malign influences’ and ‘political manipulations’, and bringing back the well-designed legislative measure broadly worded by the Assembly of the African Union which adopted as a strategic document known as the “AU Master Roadmap (AUMR) of Practical Steps to Silencing the Guns in Africa” in 2017. (See African Union report, April 2017)
A peaceful continent is possible. This aspiration inspired the ‘Silencing the Guns in Africa’ agenda, a flagship initiative of the AU Agenda 2063 that aspires to end all wars, conflict and gender-based violence, and to prevent genocide. As a long-standing partner, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), for instance, has seriously recommitted its partnerships and opportunities to further the Silencing the Guns agenda as a necessary condition for Africa’s transformative development. This focuses on the people, prosperity and peace as a basis for its contributions to AU’s aspirations across Africa, according to the UNDP’s report re-issued in February 2022.
Professor Sergiu Mișcoiu at the Faculty of European Studies, Babes-Bolyai University in Cluj-Napoca (Romania), where he serves as a Director of the Centre for International Cooperation and as Director of the Centre for African Studies, noted in an article to Global Research, that African countries are bound to wake up to a common understanding of the true meaning of their colonial past for the present and determine their future existence. In fact, the leaders and the elites have to engage in development decision-making processes, and at the same time have to play their roles as autonomous actors instead of being pawns in global politics.
Mahamat’s Strengths and Weaknesses
In my view, analyzing most of the media reports and arguments, indicated this year the role is reserved for a representative from East Africa to replace Moussa Mahamat, a veteran politician from the Republic of Chad in West Africa, who has served two terms since 2017. Before taking up this position, he was the foreign minister of Chad. As the history of the procedures indicates, the elected chairperson becomes the head of the African Union Commission. Mahamat, born on 21 June 1960, was for the first time elected as the chairperson on 30 January 2017 but assumed office in March 2017. The chairperson is elected by the Assembly for a four-year term, renewable once. During his eight years of leadership, holding executive powers, needed internal structural reforms that have popularly been called for were not simply carried out, and a record of publicly announced accomplishments grossly lacked probity and transparent accountability.
Despite that as mentioned above, the African Union under Moussa Mahamat has made several achievements including raising the continental external relations profile and its ascension into the Group of Twenty (G20). In September 2023, Prime Minister Narendra Modi of India, chairing the G20 summit, the G20 nations agreed to grant the African Union permanent membership status in an appreciable move aimed at offering the continent a stronger voice on important questions and to uplift its unto the higher stage. In its final declaration in New Delhi, the G20 granted the African Union a full-fledged membership. The G20 consists of 19 countries and the European Union, making up about 85 per cent of the global GDP and two-thirds of the world’s population.
Under the administration of Moussa Mahamat, the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), the single continental market has the potential to unite an estimated 1.4 billion people in a $2.5 trillion economic bloc. The AfCFTA opens up more tremendous opportunities for both local African and foreign investors from around the world. It aims at making Africa the largest common market in the world and accelerating continental integration. It is expected to reinforce the measures taken in terms of the free movement of persons, goods, and services across borders. But much depends on the collective determination and solidarity demonstrated, to face the challenges in a united and resolute manner, by the African leaders. It depends on the strong mobilization of African leaders and the effective coordination provided by the African Union.
Essential Leadership Attitudes
In mid-July 2024, Business & Financial Times wrote that the candidates were discreetly campaigning for the top position. The B&FT media indicated further that, despite the general qualification being former foreign ministers, and in the case of Odinga being an experienced politician and readily preferred by the majority of African leaders, some other distinguishing leadership attitude and approach are necessary and required of the candidate. Education is the cornerstone for awareness, but one of the crucial qualities that a leader must possess is the inherent positive notion of servitude, in addition to commitment to the organization’s future aspirations.
As the incoming chairperson prepares to take on the baton, it is important to look forward with optimism, eager to continue making an impact in new ways, within the geopolitical context, and be ready to strategize broadly with key stakeholders and external powers. Pragmatism should be the catch-word while ensuring pragmatic acknowledgement of the potential to drive progress and actionable initiatives. Step away from excessive symbolism and superficial (shallow) influence instead of an invaluable and impactful engagement or relations.
AU is a multilateral body, and in this critical moment for the continent plagued by high youth unemployment, weak institutions and political instability, the new leader must have the spirit of innovation, dynamism and a forward-thinking vision. Professor (Ambassador) Edward Boateng, business executive and politician, in an opinion article, listed some of the criteria for the ideal AU head as follows: (i) Inter-generational bridge: Capability to bridge generational divides within the AU, fostering inter-generational dialogue and including the perspectives of all age groups in policy-making processes.
(ii) Conflict resolution: Strong leadership in addressing conflicts and crises effectively, with a coherent strategy for conflict resolution across the continent.
(iii) Institutional reforms: Commitment to spearheading institutional reforms, enhancing financial sustainability and streamlining decision-making processes to address the AU’s bureaucratic challenges.
(iv) Economic development: Drive economic reforms, attract investment and foster a business-friendly environment to tap into Africa’s vast resources and young population.
(v) Empowerment of women and youth: Promotion of policies that enhance gender equality and provide opportunities for young people to participate in governance and economic activities.
Opening New Chapter
A new chapter characterizing plethoric changes is, however, expected under the next chairperson beginning in March 2025. Arguments for several changes are necessary to make the continental organization work more effectively and produce tangible results especially now within the context of global reconfiguration. Africa is too diverse to fit together. But there are many more interests in uniting the continent. But the political, economic, and cultural diversities have to be transformed into continental strength to ensure development and growth, instead of a noticeable display of weaknesses and passive actions. It is often repeatedly claimed that the African Union needs urgent realistic reforms and some kind of rebranding of its structure as an effective instrument for rapid development, new economic architecture, and substantial growth.
In late January 2024, Rwandan President Paul Kagamé was appointed to lead the AU institutional reforms process. It was an important step towards implementing its institutional reforms, setting the Pan-African organization’s objectives under the leadership of the Heads of State who meet once a year at the Assembly. As Africa faces a multitude and multitude of crises, so also unstoppable debates have dominated inside Africa and on international platforms over the performance of the 55-member organization, its existing challenges, and the way forward in the fast-changing world.
Appropriately four candidates were short-listed for the position based on the fact that East and Southern Africa now have their turn. But at a glance, Odinga seemingly envisions carving out a new distinctive image for the African Union. His high-value knowledge and experiences, corporate business entrepreneurialism combined with pragmatic new economic development thinking would probably save Africa. Narratives too indicated that Odinga would adopt a far-reaching overhauled approach and take unshakable measures toward most significant issues across Africa. These are essential conditions for re-imaging the AU’s future.
An in-depth analysis shows us that there should be four structural directions, in particular, to address by the next AUC chairperson: (1) investment in the economic sphere; (2) increased cooperation in the security field, and; (3) a shared vision of international and regional issues, and (4) on the social and humanitarian sphere. These represent the significant aspects of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in Africa. Therefore, the AU has to take up the task of developing collective approaches to the problems of maintaining peace and security, strengthening democratic processes, developing human potential, and ensuring socio-economic growth.
In a final summary, the AU’s vision is to accelerate progress, and spearhead development and integration in close collaboration with all members. These are incorporated into a single continental development program often referred to as the AU Agenda 2063.
Professor Maurice Okoli is a fellow at the Institute for African Studies and the Institute of World Economy and International Relations, Russian Academy of Sciences. He is also a fellow at the North-Eastern Federal University of Russia. He is an expert at the Roscongress Foundation and the Valdai Discussion Club. As an academic researcher and economist with a keen interest in current geopolitical changes and the emerging world order, Maurice Okoli frequently contributes articles for publication in reputable media portals on different aspects of the interconnection between developing and developed countries, particularly in Asia, Africa and Europe. With comments and suggestions, he can be reached via email: ma***********@***il.com.
Dr Ken Onyeali Ikpe is the former Group CEO of Insight Redefini Group, Sub-Saharan Africa’s biggest Marketing Communications & Consumer Consulting Group. He holds a Ph.D and was trained at IESE Business School in Barcelona, Spain.
Feature/OPED
How Christians Can Stay Connected to Their Faith During This Lenten Period

It’s that time of year again, when Christians come together in fasting and prayer. Whether observing the traditional Lent or entering a focused period of reflection, it’s a chance to connect more deeply with God, and for many, this season even sets the tone for the year ahead.
Of course, staying focused isn’t always easy. Life has a way of throwing distractions your way, a nosy neighbour, a bus driver who refuses to give you your change, or that colleague testing your patience. Keeping your peace takes intention, and turning off the noise and staying on course requires an act of devotion.
Fasting is meant to create a quiet space in your life, but if that space isn’t filled with something meaningful, old habits can creep back in. Sustaining that focus requires reinforcement beyond physical gatherings, and one way to do so is to tune in to faith-based programming to remain spiritually aligned throughout the period and beyond.
On GOtv, Christian channels such as Dove TV channel 113, Faith TV and Trace Gospel provide sermons, worship experiences and teachings that echo what is being practised in churches across the country.
From intentional conversations on Faith TV on GOtv channel 110 to true worship on Trace Gospel on channel 47, these channels provide nurturing content rooted in biblical teaching, worship, and life application. Viewers are met with inspiring sermons, reflections on scripture, and worship sessions that help form a rhythm of devotion. During fasting periods, this kind of consistent spiritual input becomes a source of encouragement, helping believers stay anchored in prayer and mindful of God’s presence throughout their daily routines.
To catch all these channels and more, simply subscribe, upgrade, or reconnect by downloading the MyGOtv App or dialling *288#. You can also stream anytime with the GOtv Stream App.
Plus, with the We Got You offer, available until 28th February 2026, subscribers automatically upgrade to the next package at no extra cost, giving you access to more channels this season.
Feature/OPED
Turning Stolen Hardware into a Data Dead-End

By Apu Pavithran
In Johannesburg, the “city of gold,” the most valuable resource being mined isn’t underground; it’s in the pockets of your employees.
With an average of 189 cellphones reported stolen daily in South Africa, Gauteng province has become the hub of a growing enterprise risk landscape.
For IT leaders across the continent, a “lost phone” is rarely a matter of a misplaced device. It is frequently the result of a coordinated “snatch and grab,” where the hardware is incidental, and corporate data is the true objective.
Industry reports show that 68% of company-owned device breaches stem from lost or stolen hardware. In this context, treating mobile security as a “nice-to-have” insurance policy is no longer an option. It must function as an operational control designed for inevitability.
In the City of Gold, Data Is the Real Prize
When a fintech agent’s device vanishes, the $300 handset cost is a rounding error. The real exposure lies in what that device represents: authorised access to enterprise systems, financial tools, customer data, and internal networks.
Attackers typically pursue one of two outcomes: a quick wipe for resale on the secondary market or, far more dangerously, a deep dive into corporate apps to extract liquid assets or sellable data.
Clearly, many organisations operate under the dangerous assumption that default manufacturer security is sufficient. In reality, a PIN or fingerprint is a flimsy barrier if a device is misconfigured or snatched while unlocked. Once an attacker gets in, they aren’t just holding a phone; they are holding the keys to copy data, reset passwords, or even access admin tools.
The risk intensifies when identity-verification systems are tied directly to the compromised device. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), widely regarded as a gold standard, can become a vulnerability if the authentication factor and the primary access point reside on the same compromised device. In such cases, the attacker may not just have a phone; they now have a valid digital identity.
The exposure does not end at authentication. It expands with the structure of the modern workforce.
65% of African SMEs and startups now operate distributed teams. The Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) culture has left many IT departments blind to the health of their fleet, as personal devices may be outdated or jailbroken without any easy way to know.
Device theft is not new in Africa. High-profile incidents, including stolen government hardware, reinforce a simple truth: physical loss is inevitable. The real measure of resilience is whether that loss has any residual value. You may not stop the theft. But you can eliminate the reward.
Theft Is Inevitable, Exposure is Not
If theft cannot always be prevented, systems must be designed so that stolen devices yield nothing of consequence. This shift requires structured, automated controls designed to contain risk the moment loss occurs.
Develop an Incident Response Plan (IRP)
The moment a device is reported missing, predefined actions should trigger automatically: access revocation, session termination, credential reset and remote lock or wipe.
However, such technical playbooks are only as fast as the people who trigger them. Employees must be trained as the first line of defence —not just in the use of strong PINs and biometrics, but in the critical culture of immediate reporting. In high-risk environments, containment windows are measured in minutes, not hours.
Audit and Monitor the Fleet Regularly
Control begins with visibility. Without a continuous, comprehensive audit, IT teams are left responding to incidents after damage has occurred.
Opting for tools like Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) allows IT teams to spot subtle, suspicious activities or unusual access attempts that signal a compromised device.
Review Device Security Policies
Security controls must be enforced at the management layer, not left to user discretion. Encryption, patch updates and screen-lock policies should be mandatory across corporate devices.
In BYOD environments, ownership-aware policies are essential. Corporate data must remain governed by enterprise controls regardless of device ownership.
Decouple Identity from the Device
Legacy SMS-based authentication models introduce avoidable risk when the authentication channel resides on the compromised handset. Stronger identity models, including hardware tokens, reduce this dependency.
At the same time, native anti-theft features introduced by Apple and Google, such as behavioural theft detection and enforced security delays, add valuable defensive layers. These controls should be embedded into enterprise baselines rather than treated as optional enhancements.
When Stolen Hardware Becomes Worthless
With POPIA penalties now reaching up to R10 million or a decade of imprisonment for serious data loss offences, the Information Regulator has made one thing clear: liability is strict, and the financial fallout is absolute. Yet, a PwC survey reveals a staggering gap: only 28% of South African organisations are prioritising proactive security over reactive firefighting.
At the same time, the continent is battling a massive cybersecurity skills shortage. Enterprises simply do not have the boots on the ground to manually patch every vulnerability or chase every “lost” terminal. In this climate, the only viable path is to automate the defence of your data.
Modern mobile device management (MDM) platforms provide this automation layer.
In field operations, “where” is the first indicator of “what.” If a tablet assigned to a Cape Town district suddenly pings on a highway heading out of the city, you don’t need a notification an hour later—you need an immediate response. An effective MDM system offers geofencing capabilities, automatically triggering a remote lock when devices breach predefined zones.
On Supervised iOS and Android Enterprise devices, enforced Factory Reset Protection (FRP) ensures that even after a forced wipe, the device cannot be reactivated without organisational credentials, eliminating resale value.
For BYOD environments, we cannot ignore the fear that corporate oversight equates to a digital invasion of personal lives. However, containerization through managed Work Profiles creates a secure boundary between corporate and personal data. This enables selective wipe capabilities, removing enterprise assets without intruding on personal privacy.
When integrated with identity providers, device posture and user identity can be evaluated together through multi-condition compliance rules. Access can then be granted, restricted, or revoked based on real-time risk signals.
Platforms built around unified endpoint management and identity integration enable this model of control. At Hexnode, this convergence of device governance and identity enforcement forms the foundation of a proactive security mandate. It transforms mobile fleets from distributed risk points into centrally controlled assets.
In high-risk environments, security cannot be passive. The goal is not recovery. It is irrelevant, ensuring that once a device leaves authorised hands, it holds no data, no identity leverage, and no operational value.
Apu Pavithran is the CEO and founder of Hexnode
Feature/OPED
Daniel Koussou Highlights Self-Awareness as Key to Business Success

By Adedapo Adesanya
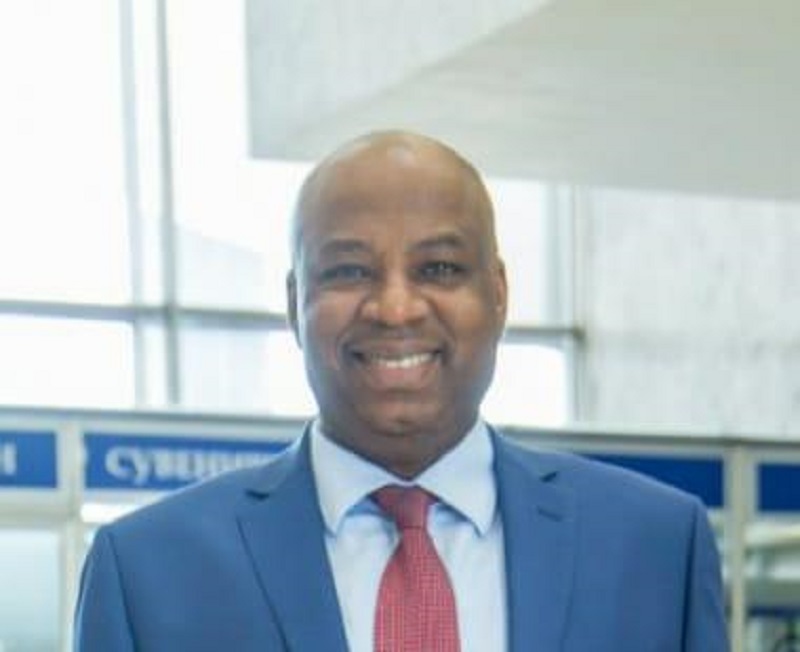
At a time when young entrepreneurs are reshaping global industries—including the traditionally capital-intensive oil and gas sector—Ambassador Daniel Koussou has emerged as a compelling example of how resilience, strategic foresight, and disciplined execution can transform modest beginnings into a thriving business conglomerate.
Koussou, who is the chairman of the Nigeria Chapter of the International Human Rights Observatory-Africa (IHRO-Africa), currently heads the Committee on Economic Diplomacy, Trade and Investment for the forum’s Nigeria chapter. He is one of the young entrepreneurs instilling a culture of nation-building and leadership dynamics that are key to the nation’s transformation in the new millennium.
The entrepreneurial landscape in Nigeria is rapidly evolving, with leaders like Koussou paving the way for innovation and growth, and changing the face of the global business climate. Being enthusiastic about entrepreneurship, Koussou notes that “the best thing that can happen to any entrepreneur is to start chasing their dreams as early as possible. One of the first things I realised in life is self-awareness. If you want to connect the dots, you must start early and know your purpose.”
Successful business people are passionate about their business and stubbornly driven to succeed. Koussou stresses the importance of persistence and resilience. He says he realised early that he had a ‘calling’ and pursued it with all his strength, “working long weekends and into the night, giving up all but necessary expenditures, and pressing on through severe setbacks.”
However, he clarifies that what accounted for an early success is not just tenacity but also the ability to adapt, to recognise and respond to rapidly changing markets and unexpected events.
Ambassador Koussou is the CEO of Dau-O GIK Oil and Gas Limited, an indigenous oil and natural gas company with a global outlook, delivering solutions that power industries, strengthen communities, and fuel progress. The firm’s operations span exploration, production, refining, and distribution.
Recognising the value of strategic alliances, Koussou partners with business like-minds, a move that significantly bolsters Dau-O GIK’s credibility and capacity in the oil industry. This partnership exemplifies the importance of building strong networks and collaborations.
The astute businessman, who was recently nominated by the African Union’s Agenda 2063 as AU Special Envoy on Oil and Gas (Continental), admonishes young entrepreneurs to be disciplined and firm in their decision-making, a quality he attributed to his success as a player in the oil and gas sector. By embracing opportunities, building strong partnerships, and maintaining a commitment to excellence, Koussou has not only achieved personal success but has also set a benchmark for future generations of African entrepreneurs.
His journey serves as a powerful reminder that with determination and vision, success is within reach.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn