General
ESG Obligations Leading to Risk of Increased Litigation for African Businesses

By Darryl Bernstein
As African businesses begin to recover and build the resilience needed to successfully navigate COVID-19 disruption, a focus on Environmental Social and Governance (ESG) strategies is proving to be essential for long-term success.
In order to stay competitive, organisations based in Africa are engaging meaningfully with ESG to build robust sustainability strategies that meet stakeholder expectations and enable compliance with global and domestic mandatory and voluntary ESG standards and codes.
ESG encompasses a broad range of issues across the spectrum of Environmental (climate change, biodiversity, waste, water and resource use, pollution), Social (human rights, labour practices, HSE, diversity); and Governance (corporate governance, ethics, compliance) matters.
As climate change impacts become clearer and nearer, there is an increasing emphasis on the Environment aspect of ESG. After the pandemic, initiatives in Africa are expected to have a heightened focus on green, low-carbon and sustainable development, via, for example, clean energy production, community care initiatives, green transport and sustainable water projects, wildlife protection programmes and low-carbon development projects.
There is a major role for ESG policies to play in mitigating some of the effects of climate change, through planning and building for hotter temperatures, higher sea levels and more extreme weather conditions, for example.
Organisations are adopting new strategies that address climate change risk and identify the sustainable opportunities that arise from addressing climate concerns. To regulate this, there are likely to be developments from African regulators in the near future that address climate risk disclosure requirements for businesses operating on the continent.
Post-pandemic, the discussions around ESG are also resulting in an added emphasis on the Social aspect – which, among other things, focuses on protecting an organisation’s workers and the wider local populations in which these businesses are based.
Organisations are looking at ways to build better social programmes that are more resilient to future pandemics and ensure good business practice. A focus on issues such as enhancing considerations around the health and safety of employees and communities, implementing diverse and inclusive workplace cultures, and building good management teams that can pull employees together in all kinds of remote, physical workplace and hybrid settings, put companies in a strong position to move forward.
The Governance aspect has also been emphasized by the pandemic, with an increased focus on due diligence around compliance with regards to anti-bribery and corruption, data privacy and cyber security legislation, for example.
Some of the larger African jurisdictions have already implemented mandatory ESG and sustainability reporting frameworks and, going forward, more African regulators are expected to replace current voluntary frameworks with mandatory ones or to adopt new mandatory frameworks. In turn, organisations operating in Africa will seek guidance and more detail from corporate regulators on how they want to see ESG reported and the practices behind the reporting process.
In South Africa, there are many laws that govern ESG factors, including business and financial sector conduct, economic and social empowerment and environmental protection. Voluntary codes such as the King IV Code on corporate governance and the Code for Responsible Investing in South Africa also serve as a guide to businesses on ESG considerations.
Other examples include Kenya, where the Capital Markets Authority introduced Stewardship and Corporate Governance Codes in 2017 and Nigeria, where the Nigerian Code of Corporate Governance was introduced in 2019. Globally, in addition to numerous country-specific laws, there are a plethora of voluntary sustainability-focused codes and standards, including the UN Guiding Principles on Business and the Human Rights and UN Guiding Principles Reporting Framework.
ESG risk management has become a mainstream component of corporate due diligence programmes, and corporate boards are being held accountable for their ESG practices by their shareholders, stakeholders and management teams. Risks for non-compliance with the multitude of global and local laws, voluntary codes and best practices governing ESG factors range from criminal prosecution and hefty fines to reputational risk and business failure as a result of not fulfilling ESG commitments.
Actual and perceived non-compliance with ESG regulations and best practices have engendered activist shareholder protests and action against the parent companies of global groups. A key challenge for businesses is navigating where the laws end, and business strategy and market expectations begin. This is especially the case when navigating the major global issues of, for example, environmental standards and human rights responsibilities. Such issues often lead to activism, litigation and class actions if a business falls short of sustainability standards or appears to be breaking publicly made promises.
Contractual liabilities around ESG must be carefully considered, as contracts that stipulate compliance with certain standards can trigger a breach of contract claim if there is seen to be any violation of the terms. It would be better for businesses to ensure in advance that they can fulfil specific ESG obligations before agreeing to them contractually. Limitations of liability should also be agreed upon to mitigate the risks.
Further, if companies have made public promises regarding their ESG obligations and they are seen to be not fulfilling such obligations, they could be vulnerable to the threat of class actions that are brought by consumers and shareholder activists. Companies should identify what ESG goals can be properly measured, and what goals should be clearly defined as being aspirational and ensure that this is accurately communicated in the public domain. Reputational damage from ESG non-compliance escalates quickly and can be difficult to recover from.
For African organisations, maintaining a long-term sustainability strategy ensures sound financial performance, full compliance with local and global laws and frameworks, and substantially increased resilience in a challenging post-pandemic environment. In the current global environment, ESG is no longer just about doing the right thing, the dial has shifted and having a legally sound and comprehensive approach to ESG considerations is a prerequisite for business success.
Darryl Bernstein is a Partner and Head of the Dispute Resolution Practice at Baker McKenzie in Johannesburg
General
Deep Blue Project: Mobereola Seeks Air Force Support
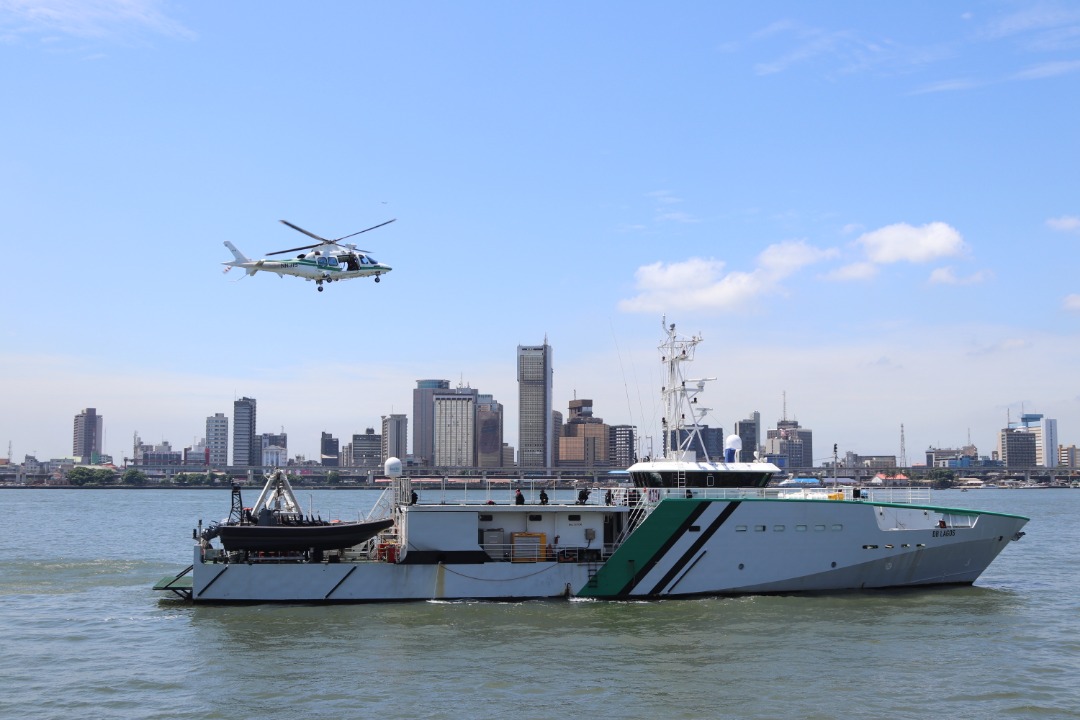

By Adedapo Adesanya
The Director General of the Nigerian Maritime Administration and Safety Agency (NIMASA), Mr Dayo Mobereola, is seeking enhanced cooperation between the agency and the Nigerian Air Force (NAF) with the aim of strengthening tactical air support within the Deep Blue project.
During a courtesy visit last week, Mr Mobereola told the Chief of Air Staff, Air Marshall S. K. Aneke at the NAF Headquarters in Abuja, that the Air Force was a strategic partner in enhancing maritime security in Nigeria and sustaining the momentum of the Deep Blue Project’s success.
According to the DG, “We are here to seek the Air Force’s support, given the importance of tactical air surveillance to the Deep Blue Project. Nigeria is the only African country with a record of zero piracy within the last 4 years. The Deep Blue Project platforms have been used to achieve zero piracy and sea robberies in the Gulf of Guinea, and we need your collaboration to sustain this momentum”.
He further emphasised that international trade depends on security, which is why vessels prefer to go to or transit through countries where they are secured. “With the traffic we have now, we need to show more security might through collaboration to strengthen our trade viability because of the risks attached to our route. We need these collaborations to sustain what we have achieved so far with the Deep Blue Project”.
The NIMASA DG expressed hope that the collaboration with the Nigeria Air Force will reduce response time.
On his part, the Chief of Air Staff, Air Marshall S.K. Aneke, noted that the Air Force desires to be “a very supportive and collaborative partner with NIMASA and is ready to match the Agency step by step and side by side to achieve the desired results.”
He noted that “collaboration between NIMASA and the Nigerian Air Force under the Deep Blue Project can be strengthened through a joint strategic framework, integrated command structures, and a standing steering committee to ensure shared objectives and accountability.
“Establishing a joint maritime domain awareness fusion cell will enable real-time intelligence sharing, synchronised surveillance, and faster response to maritime threats and ensure sustained operational effectiveness across Nigeria’s territorial waters and exclusive economic zone,” he said, according to a statement.
The Air Force Chief added that the Air Force can also support NIMASA outside the Deep Blue Project operations by providing its own ISR platforms, tactical air support, and rapid airborne deployment for interdictions and search and rescue missions.
While thanking the NIMASA DG for the basic trainings the Agency has provided the aircraft pilots under the Deep Blue Project, Air Marshall Aneke also highlighted areas of operational challenges needing NIMASA’s attention to include bridging the communication gap between NAF operators and NIMASA, higher level and in-depth maintenance trainings, readily available fueling of aircrafts to avoid delays on missions, and provision of flying kits among others.
He therefore pledged the Air Force’s collaboration and assured that the request by NIMASA has been noted and that things will begin to move at thrice its speed going forward.
General
Nigeria’s Democracy Suffocating Under Tinubu—Atiku

By Modupe Gbadeyanka
Former Vice President, Mr Atiku Abubakar, has lambasted the administration of President Bola Tinubu for the turnout at the FCT Area Council elections held last Saturday.
In a statement signed by his Media Office, the Adamawa-born politician claimed that the health of Nigeria’s democracy under the current administration was under threat.
According to him, “When citizens lose faith that their votes matter, democracy begins to die. What we are witnessing is not mere voter apathy. It is a direct consequence of an administration that governs with a chokehold on pluralism. Democracy in Nigeria is being suffocated slowly, steadily, and dangerously.”
He warned that the steady erosion of participatory governance, if left unchecked, could inflict irreversible damage on the democratic fabric painstakingly built over decades.
“A democracy without vibrant opposition, without free political competition, and without public confidence is democracy in name only. If this chokehold is not released, history will record this era as the period when our hard-won freedoms were traded for fear and conformity,” he stressed.
Mr Atiku said the turnout for the poll was below 20 per cent, with the Abuja Municipal Area Council (AMAC) recording 7.8 per cent.
He noted that such civic participation in the nation’s capital, the symbolic heartbeat of the federation, is not accidental, as it is the predictable outcome of a political environment poisoned by intolerance, intimidation, and the systematic weakening of opposition voices.
The presidential candidate of the People’s Democratic Party (PDP) in the 2023 general elections stated that the ruling All Progressives Congress (APC) under Mr Tinubu has pursued a deliberate policy of shrinking democratic space, harassing dissenters, coercing defectors, and fostering a climate where alternative political viewpoints are treated as threats rather than contributions to national development.
He called on opposition parties and democratic forces across the country to urgently close ranks and forge a united front, declaring, “This is no longer about party lines; it is about preserving the Republic. The time to stand together to rescue and rebuild Nigeria is now.”
General
Nigeria Eyes Full Entry into Council of Palm Oil Producing Countries

By Adedapo Adesanya
Nigeria is set to validate a technical committee report geared towards transitioning the country from observer status to full membership of the Council of Palm Oil Producing Countries (CPOPC) in April.
Mr Abubakar Kyari, Minister of Agriculture and Food Security, said this when the council’s mission visited him over the weekend in Abuja, noting that the ministry had constituted a technical committee to consider how the country would seamlessly transit from observer country to membership in CPOPC based on its strategic importance in palm oil production.
“We are conscious of the fact that the palm oil value chain is very strategic for us and identified it as an export crop that can drive foreign exchange for the country and ensure good health in terms of consumption.
“We are conscious of the fact that we need the support of CPOPC countries to provide the country with a new variety of seeds that are climate-smart and resistant so that they can be produced by farmers in the country,” he said.
Mr Alphonsus Inyang, President, National Palm Produce Association of Nigeria (NPPAN), said being a member of CPOPC Nigeria would target over 10 million tonnes of oil palm between 2026 and 2050.
“We are also targeting 2.5 million hectares from among Nigeria households who are out to produce one hectare each, geared towards a N20 trillion annual economy within this period from among Nigeria households.
“We are working side by side with the big players who will be developing plantations,” he said.
The Secretary-General of CPOPC, Ms Izzana Salleh, said the council’s mission to Nigeria was to see how the country could transit from observer status to full membership, among others
She said that the status of the country as an observer nation since 2024 would expire by November.
Ms Salleh assured the country of the council’s readiness to support its vision to strengthen domestic production, enhance food security and build a competitive and sustainable palm oil supply chain.
The official emphasised that being a member of the council would strategically position Nigeria for a greater future regarding oil palm production.
According to her, the visit is to strengthen the council’s engagement with Nigeria, including potential membership in CPOPC.
She said: “The council’s mission to Nigeria aims to advance both Nigeria’s national ambitions and Africa’s collective voice in global agricultural discussions.
“CPOPC was established to promote cooperation among producing nations, empower smallholders, advance sustainability, and ensure fair, science-based global dialogue on vegetable oils.
She emphasised that being a member of the council would strategically position the country for greater future prospects regarding oil palm production and the value chain, as well as export.
“We are ready to support Nigeria’s vision to strengthen domestic production, enhance food security, and build a competitive and sustainable palm oil supply chain,” she said.
-

 Feature/OPED6 years ago
Feature/OPED6 years agoDavos was Different this year
-
Travel/Tourism10 years ago
Lagos Seals Western Lodge Hotel In Ikorodu
-

 Showbiz3 years ago
Showbiz3 years agoEstranged Lover Releases Videos of Empress Njamah Bathing
-

 Banking8 years ago
Banking8 years agoSort Codes of GTBank Branches in Nigeria
-

 Economy3 years ago
Economy3 years agoSubsidy Removal: CNG at N130 Per Litre Cheaper Than Petrol—IPMAN
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoSort Codes of UBA Branches in Nigeria
-

 Banking3 years ago
Banking3 years agoFirst Bank Announces Planned Downtime
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoHighest Paid Nigerian Footballer – How Much Do Nigerian Footballers Earn